Gas6/Axl signaling attenuates alveolar inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by up-regulating SOCS3-mediated pathway
- PMID: 31318922
- PMCID: PMC6638944
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219788
Gas6/Axl signaling attenuates alveolar inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by up-regulating SOCS3-mediated pathway
Abstract
Background: Axl is a cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase, and activation of the Axl attenuates inflammation induced by various stimuli. Growth arrest-specific 6 (Gas6) has high affinity for Axl receptor. The role of Gas6/Axl signaling in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury (IR-ALI) has not been explored previously. We hypothesized that Gas6/Axl signaling regulates IR-induced alveolar inflammation via a pathway mediated by suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3).
Methods: IR-ALI was induced by producing 30 min of ischemia followed by 90 min of reperfusion in situ in an isolated and perfused rat lung model. The rats were randomly allotted to a control group and IR groups, which were treated with three different doses of Gas6. Mouse alveolar epithelium MLE-12 cells were cultured in control and hypoxia-reoxygenation (HR) conditions with or without Gas6 and Axl inhibitor R428 pretreatment.
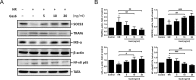
Results: We found that Gas6 attenuated IR-induced lung edema, the production of proinflammatory cytokines in perfusates, and the severity of ALI ex vivo. IR down-regulated SOCS3 expression and up-regulated NF-κB, and Gas6 restored this process. In the model of MLE-12 cells with HR, Gas6 suppressed the activation of TRAF6 and NF-κB by up-regulating SOCS3. Axl expression of alveolar epithelium was suppressed in IR-ALI but Gas6 restored phosphorylation of Axl. The anti-inflammatory effect of Gas6 was antagonized by R428, which highlighted that phosphorylation of Axl mediated the protective role of Gas6 in IR-ALI.
Conclusions: Gas6 up-regulates phosphorylation of Axl on alveolar epithelium in IR-ALI. The Gas6/Axl signaling activates the SOCS3-mediated pathway and attenuates IR-related inflammation and injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Inhibition of NKCC1 Modulates Alveolar Fluid Clearance and Inflammation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Lung Injury via TRAF6-Mediated Pathways.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 13;9:2049. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02049. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30271405 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Axl attenuates acute kidney injury by alleviating inflammation via SOCS3 downregulation in tubular epithelial cells.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04222-z. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40597777 Free PMC article.
-
Axl activation attenuates neuroinflammation by inhibiting the TLR/TRAF/NF-κB pathway after MCAO in rats.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Feb;110:59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.11.009. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29196212 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of the Gas6/Axl Signaling Pathway in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 15;22(18):9953. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189953. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the vitamin K-dependent growth factor Gas6 in glomerular pathophysiology.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004 Jul;13(4):465-70. doi: 10.1097/01.mnh.0000133981.63053.e9. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004. PMID: 15199298 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between Akt and NF-κB pathway mediates inhibitory effect of gas6 on monocytes-endothelial cells interactions stimulated by P. gingivalis-LPS.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jul;24(14):7979-7990. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15430. Epub 2020 May 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32462812 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of Gas6 attenuates lung fibrosis via inhibition of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibroblast activation.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Apr 5;40(1):20. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09858-5. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38578518 Free PMC article.
-
Gas6 Ameliorates Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis in Bleomycin-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 12;9(11):1674. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111674. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829903 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SOCS3 and PTGS2 as new biomarkers for the diagnosis of gout by cross-species comprehensive analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 23;10(9):e30020. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30020. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38707281 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Networks, Management Approaches, and Emerging Treatments of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Nov 8;2022:6799414. doi: 10.1155/2022/6799414. eCollection 2022. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36397950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- den Hengst WA, Gielis JF, Lin JY, Van Schil PE, De Windt LJ, Moens AL. Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury: a molecular and clinical view on a complex pathophysiological process. American Journal of Physiology—Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2010;299(5):H1283–H99. 10.1152/ajpheart.00251.2010 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

