Hydrophobic *BEA-Type Zeolite Membranes on Tubular Silica Supports for Alcohol/Water Separation by Pervaporation
- PMID: 31319501
- PMCID: PMC6680943
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes9070086
Hydrophobic *BEA-Type Zeolite Membranes on Tubular Silica Supports for Alcohol/Water Separation by Pervaporation
Abstract
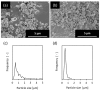
Hydrophobic pure-silica *BEA-type zeolite membranes with large pores were prepared on tubular silica supports by hydrothermal synthesis using a secondary growth method and were applied to the separation of alcohol/water mixtures by pervaporation (PV), an alternative energy-efficient process for production of biofuels. Amorphous pure-silica tubular silica supports, free of Al atoms, were used for preparing the membranes. In this study, the effects of the synthesis conditions, such as the H2O/SiO2 and NH4F/SiO2 ratios in the synthetic gel, on the membrane formation process and separation performance were systematically investigated. The successfully prepared dense and continuous membranes exhibited alcohol selectivity and high flux for the separation of ethanol/water and butanol/water mixtures. The pure-silica *BEA membranes obtained under optimal conditions (0.08SiO2:0.5TEAOH:0.7NH4F:8H2O) showed high PV performance with a separation factor of 229 and a flux of 0.62 kg·m-2·h-1 for a 1 wt % n-butanol/water mixture at 318 K. This result was attributed to the hydrophobicity and large pore size of the pure-silica *BEA membrane. This was the first successful synthesis of hydrophobic large-pore zeolite membranes on tubular supports with alcohol selectivity, and the obtained results could provide new insights into the research on hydrophobic membranes with high permeability.
Keywords: *BEA-type zeolite; alcohol selectivity; butanol; electrophoretic deposition; ethanol; hydrophobic zeolite membrane; hydrothermal synthesis; pervaporation separation; secondary growth; tubular silica support.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Bowen T.C., Noble R.D., Falconer J.L. Fundamentals and applications of pervaporation through zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004;245:1–33. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2004.06.059. - DOI
-
- Sano T., Yanagishita H., Kiyozumi Y., Mizukami F., Haraya K. Separation of ethanol/water mixture by silicalite membrane on pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1994;95:221–228. doi: 10.1016/0376-7388(94)00120-0. - DOI
-
- Nomura M., Yamaguchi T., Nakao S.I. Ethanol/water transport through silicalite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1998;144:161–171. doi: 10.1016/S0376-7388(98)00043-X. - DOI
-
- Chen H., Li Y., Yang W. Preparation of silicalite-1 membrane by solution-filling method and its alcohol extraction properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2007;296:122–130. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2007.03.021. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

