Regulation of Epithelial Cell Functions by the Osmolality and Hydrostatic Pressure Gradients: A Possible Role of the Tight Junction as a Sensor
- PMID: 31319610
- PMCID: PMC6678979
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20143513
Regulation of Epithelial Cell Functions by the Osmolality and Hydrostatic Pressure Gradients: A Possible Role of the Tight Junction as a Sensor
Abstract
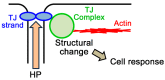
Epithelia act as a barrier to the external environment. The extracellular environment constantly changes, and the epithelia are required to regulate their function in accordance with the changes in the environment. It has been reported that a difference of the environment between the apical and basal sides of epithelia such as osmolality and hydrostatic pressure affects various epithelial functions including transepithelial transport, cytoskeleton, and cell proliferation. In this paper, we review the regulation of epithelial functions by the gradients of osmolality and hydrostatic pressure. We also examine the significance of this regulation in pathological conditions especially focusing on the role of the hydrostatic pressure gradient in the pathogenesis of carcinomas. Furthermore, we discuss the mechanism by which epithelia sense the osmotic and hydrostatic pressure gradients and the possible role of the tight junction as a sensor of the extracellular environment to regulate epithelial functions.
Keywords: cancer; hydrostatic pressure; osmolality; sensor; tight junction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hydrostatic pressure regulates tight junctions, actin cytoskeleton and transcellular ion transport.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Dec 25;390(4):1315-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.144. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19879247
-
Effects of Osmolality on Paracellular Transport in MDCK II Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 17;11(11):e0166904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166904. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27855213 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Hydrostatic Pressure on Carcinogenic Properties of Epithelia.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 30;10(12):e0145522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145522. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26716691 Free PMC article.
-
The tight junction and the epithelial barrier in coeliac disease.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2021;358:105-132. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2020.09.010. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33707052 Review.
-
Apical cytoskeletons and junctional complexes as a combined system in epithelial cell sheets.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017 Oct;1405(1):32-43. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13432. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017. PMID: 28763830 Review.
Cited by
-
Compressive stress gradients direct mechanoregulation of anisotropic growth in the zebrafish jaw joint.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Feb 8;20(2):e1010940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010940. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38330044 Free PMC article.
-
Claudin 19 Is Regulated by Extracellular Osmolality in Rat Kidney Inner Medullary Collecting Duct Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 7;20(18):4401. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184401. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31500238 Free PMC article.
-
Recellularization of Acellular Xeno Kidney Scaffold: An In Vivo Method to Generate Bioartificial Kidney.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1450:77-92. doi: 10.1007/5584_2023_785. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 37610657
-
Coordination of LMO7 with FAK Signaling Sustains Epithelial Integrity in Renal Epithelia Exposed to Osmotic Pressure.Cells. 2022 Nov 28;11(23):3805. doi: 10.3390/cells11233805. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497072 Free PMC article.
-
The Urothelium: Life in a Liquid Environment.Physiol Rev. 2020 Oct 1;100(4):1621-1705. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00041.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Physiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32191559 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

