Key role of UBQLN2 in pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia
- PMID: 31319884
- PMCID: PMC6889556
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-019-0758-7
Key role of UBQLN2 in pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia
Abstract
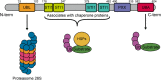
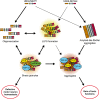
Ubiquilin-2 (UBQLN2) is a member of the ubiquilin family, actively implicated in the degradation of misfolded and redundant proteins through the ubiquitin-proteasome system and macroautophagy. UBQLN2 received much attention after the discovery of gene mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (ALS/FTD). The abnormal presence of positive UBQLN2 inclusion in the cytosol of degenerating motor neurons of familial and sporadic forms of ALS patients has been newly related to neurodegeneration. Only recently, data have emerged on its role in liquid-liquid phase separation, in stress granule development and in the formation of secondary amyloid structures. Furthermore, several animal models are available to investigate its involvement in TDP-43 pathology and neuroinflammation in ALS. This review addresses the molecular pathogenetic pathways involving UBQLN2 abnormalities which are converging toward defects in clearance mechanisms. UBQLN2.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); Animal models; Autophagy; TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43); Ubiquilin-2 (UBQLN2); Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cassel JA, Reitz AB. Ubiquilin-2 (UBQLN2) binds with high affinity to the C-terminal region of TDP-43 and modulates TDP-43 levels in H4 cells: characterization of inhibition by nucleic acids and 4-aminoquinolines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1834(6):964–971. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.03.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

