Vernakalant in Atrial Fibrillation: A Relatively New Weapon in the Armamentarium Against an Old Enemy
- PMID: 31320795
- PMCID: PMC6610431
- DOI: 10.1177/1177392819861114
Vernakalant in Atrial Fibrillation: A Relatively New Weapon in the Armamentarium Against an Old Enemy
Abstract
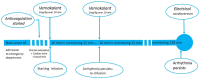
Atrial fibrillation is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, and its prevalence is increasing with age; also it is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Rhythm control is advised in recent-onset atrial fibrillation, and in highly symptomatic patients, also in young and active individuals. Moreover, rhythm control is associated with lower incidence of progression to permanent atrial fibrillation. Vernakalant is a relatively new anti-arrhythmic drug that showed efficacy and safety in recent-onset atrial fibrillation. Vernakalant is indicated in atrial fibrillation (⩽7 days) in patients with no heart disease (class I, level A) or in patients with mild or moderate structural heart disease (class IIb, level B). Moreover, Vernakalant may be considered for recent-onset atrial fibrillation (⩽3 days) post cardiac surgery (class IIb, level B). Although it is mainly indicated in patients with recent-onset atrial fibrillation and with no structural heart disease, it can be given in moderate stable cardiac disease as alternative to Amiodarone. Similarly to electrical cardioversion, pharmacological cardioversion requires a minimal evaluation and cardioversion should be included in a comprehensive management strategy for better outcome.
Keywords: Vernakalant; atrial; cardioversion; fibrillation; pharmaceutical.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Naccarelli GV, Varker H, Lin J, Schulman KL. Increasing prevalence of atrial fibrillation and flutter in the United States. Am J Cardiol. 2009;104:1534–1539. - PubMed
-
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Europace. 2016;18:1609–1678. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JL, Halperin JL, Albert NM, et al. Management of patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:1935–1944. - PubMed
-
- Manolis AS. Rhythm or rate control management of atrial fibrillation: an overrated dilemma. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2015;56:495–500. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

