Human GABRG2 generalized epilepsy: Increased somatosensory and striatothalamic connectivity
- PMID: 31321301
- PMCID: PMC6563517
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000340
Human GABRG2 generalized epilepsy: Increased somatosensory and striatothalamic connectivity
Abstract
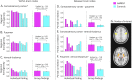
Objective: To map functional MRI (fMRI) connectivity within and between the somatosensory cortex, putamen, and ventral thalamus in individuals from a family with a GABAergic deficit segregating with febrile seizures and genetic generalized epilepsy.
Methods: We studied 5 adults from a family with early-onset absence epilepsy and/or febrile seizures and a GABAA receptor subunit gamma2 pathogenic variant (GABRG2[R43Q]) vs 5 age-matched controls. We infer differences between participants with the GABRG2 pathogenic variant and controls in resting-state fMRI connectivity within and between the somatosensory cortex, putamen, and ventral thalamus.
Results: We observed increased fMRI connectivity within the somatosensory cortex and between the putamen and ventral thalamus in all individuals with the GABRG2 pathogenic variant compared with controls. Post hoc analysis showed less pronounced changes in fMRI connectivity within and between the primary visual cortex and precuneus.
Conclusions: Although our sample size was small, this preliminary study suggests that individuals with a GABRG2 pathogenic variant, raising risk of febrile seizures and generalized epilepsy, display underlying increased functional connectivity both within the somatosensory cortex and in striatothalamic networks. This human network model aligns with rodent research and should be further validated in larger cohorts, including other individuals with generalized epilepsy with and without known GABA pathogenic variants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpressing wild-type γ2 subunits rescued the seizure phenotype in Gabrg2+/Q390X Dravet syndrome mice.Epilepsia. 2017 Aug;58(8):1451-1461. doi: 10.1111/epi.13810. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28586508 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathogenic Basis for GABRG2 Mutations Associated With a Spectrum of Epilepsy Syndromes, From Generalized Absence Epilepsy to Dravet Syndrome.JAMA Neurol. 2016 Aug 1;73(8):1009-16. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0449. JAMA Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27367160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+): clinical spectrum in seven Italian families unrelated to SCN1A, SCN1B, and GABRG2 gene mutations.Epilepsia. 2004 Feb;45(2):149-58. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.04303.x. Epilepsia. 2004. PMID: 14738422
-
A novel GABRG2 mutation, p.R136*, in a family with GEFS+ and extended phenotypes.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Apr;64:131-141. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.12.013. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24407264 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant GABA(A) receptor subunits in genetic (idiopathic) epilepsy.Prog Brain Res. 2014;213:55-85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63326-2.00003-X. Prog Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 25194483 Review.
Cited by
-
Resting-state functional MRI in pediatric epilepsy: a narrative review.Childs Nerv Syst. 2025 Feb 18;41(1):116. doi: 10.1007/s00381-025-06774-9. Childs Nerv Syst. 2025. PMID: 39964613 Review.
-
Altered dynamic functional connectivity of motor cerebellum with sensorimotor network and default mode network in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 6;15:1373125. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1373125. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38903166 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Connectivity of the Brain Across Rodents and Humans.Front Neurosci. 2022 Mar 8;16:816331. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.816331. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35350561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marini C, Harkin LA, Wallace RH, Mulley JC, Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF. Childhood absence epilepsy and febrile seizures: a family with a GABAA receptor mutation. Brain 2003;126:230–240. - PubMed
-
- Fedi M, Berkovic SF, Macdonell RAL, Curatolo JM, Marini C, Reutens DC. Intracortical hyperexcitability in humans with a GABAA receptor mutation. Cereb Cortex 2008;18:664–669. - PubMed
-
- Fedi M, Berkovic SF, Marini C, Mulligan R, Tochon-Danguy H, Reutens DC. A GABAA receptor mutation causing generalized epilepsy reduces benzodiazepine receptor binding. Neuroimage 2006;32:995–1000. - PubMed
-
- Wimmer VC, Li MYS, Berkovic SF, Petrou S. Cortical microarchitecture changes in genetic epilepsy. Neurology 2015;84:1308–1316. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
