Measuring Aging and Identifying Aging Phenotypes in Cancer Survivors
- PMID: 31321426
- PMCID: PMC7962788
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djz136
Measuring Aging and Identifying Aging Phenotypes in Cancer Survivors
Abstract
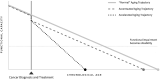
Observational data have shown that some cancer survivors develop chronic conditions like frailty, sarcopenia, cardiac dysfunction, and mild cognitive impairment earlier and/or at a greater burden than similarly aged individuals never diagnosed with cancer or exposed to systemic or targeted cancer therapies. In aggregate, cancer- and treatment-related physical, cognitive, and psychosocial late- and long-term morbidities experienced by cancer survivors are hypothesized to represent accelerated or accentuated aging trajectories. However, conceptual, measurement, and methodological challenges have constrained efforts to identify, predict, and mitigate aging-related consequences of cancer and cancer treatment. In July 2018, the National Cancer Institute convened basic, clinical, and translational science experts for a think tank titled "Measuring Aging and Identifying Aging Phenotypes in Cancer Survivors." Through the resulting deliberations, several research and resource needs were identified, including longitudinal studies to examine aging trajectories that include detailed data from before, during, and after cancer treatment; mechanistic studies to elucidate the pathways that lead to the emergence of aging phenotypes in cancer survivors; long-term clinical surveillance to monitor survivors for late-emerging effects; and tools to integrate multiple data sources to inform understanding of how cancer and its therapies contribute to the aging process. Addressing these needs will help expand the evidence base and inform strategies to optimize healthy aging of cancer survivors.
Published by Oxford University Press 2019. This work is written by US Government employees and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures
References
-
- DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(4):252–271. - PubMed
-
- Henderson TO, Ness KK, Cohen HJ. Accelerated aging among cancer survivors: from pediatrics to geriatrics. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2014;e423–e430. - PubMed
-
- Hurria A, Jones L, Muss HB. Cancer treatment as an accelerated aging process: assessment, biomarkers, and interventions. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2016;35:e516–e522. - PubMed
-
- Armenian SH, Gibson CJ, Rockne RC, Ness KK. Premature aging in young cancer survivors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111(3):226–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 CA137788/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA200859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG057545/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG052964/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA172119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197289/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA132378/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021334/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028716/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA215405/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG054849/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA180175/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG053198/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA174794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States