Sustained high HIV case-finding through index testing and partner notification services: experiences from three provinces in Zimbabwe
- PMID: 31321918
- PMCID: PMC6639671
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.25321
Sustained high HIV case-finding through index testing and partner notification services: experiences from three provinces in Zimbabwe
Abstract
Introduction: Several countries in southern Africa have made significant progress towards reaching the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS goal of ensuring that 90% of people living with HIV are aware of their status. In Zimbabwe, progress towards this "first 90" was estimated at 73% in 2016. To reach the remaining people living with HIV who have undiagnosed infection, the Zimbabwe Ministry of Health and Child Care has been promoting index testing and partner notification services (PNS). We describe the implementation of index testing and PNS under the Zimbabwe HIV Care and Treatment (ZHCT) project and the resulting uptake, HIV positivity rate and links to HIV treatment.
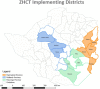
Methods: The ZHCT project has been implemented since March 2016, covering a total of 12 districts in three provinces. To assess the project's performance on index testing, we extracted data on HIV testing from the district health information system (DHIS 2) from March 2016 to May 2018, validated it using service registers and calculated monthly HIV positivity rates using Microsoft Excel. Data were disaggregated by district, province, sex and service delivery point. We used SPSS to assess for statistical differences in paired monthly HIV positivity rates by sex, testing site, and province.
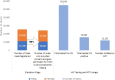
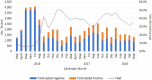
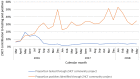
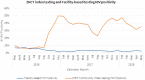
Results: The average HIV positivity rate rose from 10% during the first six months of implementation to more than 30% by August 2016 and was sustained above 30% through May 2018. The overall facility HIV positivity rate was 4.1% during the same period. The high HIV positivity rate was achieved for both males and females (mean monthly HIV positivity rate of 31.3% for males and 33.7% for females), with females showing significantly higher positivity compared to males (p < 0.001). The ZHCT mean monthly HIV positivity rate from index testing (32.6%) was significantly higher than that achieved through provider-initiated testing and counselling and other facility HIV testing modalities (4.1%, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The ZHCT project has demonstrated successes in implementing index testing and PNS by attaining a high HIV positivity rate sustained over the study period. As the country moves towards HIV epidemic control, index testing and PNS are critical strategies for targeted HIV case identification.
Keywords: HIV; HIV positivity; Zimbabwe; index testing; partner notification services.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International AIDS Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High HIV Positivity Rates Following Large-Scale HIV Self-Testing Implementation in Zimbabwe, 2018-2020.Front Public Health. 2021 Mar 23;9:606376. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.606376. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33834013 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of clients Strategic Index Case Testing on community-based detection of HIV infections (STRICT study).Int J Infect Dis. 2018 Sep;74:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.06.018. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Int J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30100537
-
Enhancing an HIV index case testing passive referral model through a behavioural skills-building training for healthcare providers: a pre-/post-assessment in Mangochi District, Malawi.J Int AIDS Soc. 2019 Jul;22 Suppl 3(Suppl Suppl 3):e25292. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25292. J Int AIDS Soc. 2019. PMID: 31321917 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation experiences and insights from the scale-up of an HIV assisted partner notification intervention in Central Asia.J Int AIDS Soc. 2019 Jul;22 Suppl 3(Suppl Suppl 3):e25313. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25313. J Int AIDS Soc. 2019. PMID: 31321890 Free PMC article.
-
Provision of HIV testing services and its impact on the HIV positivity rate in the public health sector in KwaZulu-Natal: a ten-year review.SAHARA J. 2024 Dec;21(1):2318797. doi: 10.1080/17290376.2024.2318797. Epub 2024 Feb 19. SAHARA J. 2024. PMID: 38374664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High HIV Positivity Rates Following Large-Scale HIV Self-Testing Implementation in Zimbabwe, 2018-2020.Front Public Health. 2021 Mar 23;9:606376. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.606376. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33834013 Free PMC article.
-
"It is a process" - a qualitative evaluation of provider acceptability of HIV assisted partner services in western Kenya: experiences, challenges, and facilitators.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 May 7;22(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08024-z. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 35525931 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of index HIV self-testing for sexual partners of clients enrolled in antiretroviral therapy (ART) programs in Malawi: A randomized controlled trial.PLoS Med. 2023 Aug 4;20(8):e1004270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004270. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Med. 2023. PMID: 37540649 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Providing HIV-assisted partner services to partners of partners in western Kenya: an implementation science study.J Int AIDS Soc. 2024 Jul;27 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):e26280. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26280. J Int AIDS Soc. 2024. PMID: 38965979 Free PMC article.
-
Improving HIV Case Finding Through Index Testing: Findings from Health Facilities in 12 Districts of South Africa, October 2019-September 2021.AIDS Behav. 2024 May;28(5):1708-1718. doi: 10.1007/s10461-024-04269-3. Epub 2024 Feb 15. AIDS Behav. 2024. PMID: 38358586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS . 90‐90‐90: An ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2014.
-
- ICAP at Columbia University [Internet]. Population‐based HIV impact assessment (PHIA) Project. [cited 2018 Oct 2]. Available from: https://phia.icap.columbia.edu/
-
- Sweat M, Morin S, Celentano D, Mulawa M, Singh B, Mbwambo J, et al. Community‐based intervention to increase HIV testing and case detection in people aged 16–32 years in Tanzania, Zimbabwe, and Thailand (NIMH Project Accept, HPTN 043): a randomised study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011;11:525–32. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

