Activatable Hybrid Polyphosphazene-AuNP Nanoprobe for ROS Detection by Bimodal PA/CT Imaging
- PMID: 31321973
- PMCID: PMC7039041
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.9b08386
Activatable Hybrid Polyphosphazene-AuNP Nanoprobe for ROS Detection by Bimodal PA/CT Imaging
Abstract
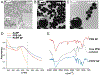
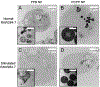
Overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is often related to inflammation or cancer and can cause tissue damage. Probes that have been previously reported to image ROS typically rely on imaging techniques that have low depth penetration in tissue, thus limiting their use to superficial disease sites. We report herein a novel formulation of hybrid nanogels loaded with gold nanoparticles (AuNP) to produce contrast for computed tomography (CT) and photoacoustics (PA), both being deep-tissue imaging techniques. The polyphosphazene polymer has been designed to selectively degrade upon ROS exposure, which triggers a switch-off of the PA signal by AuNP disassembly. This ROS-triggered degradation of the nanoprobes leads to a significant decrease in the PA contrast, thus allowing ratiometric ROS imaging by comparing the PA to CT signal. Furthermore, ROS imaging using these nanoprobes was applied to an in vitro model of inflammation, that is, LPS-stimulated macrophages, where ROS-triggered disassembly of the nanoprobe was confirmed via reduction of the PA signal. In summary, these hybrid nanoprobes are a novel responsive imaging agent that have the potential to image ROS overproduction by comparing PA to CT contrast.
Keywords: ROS; computed tomography; gold nanoparticles; photoacoustic; polyphosphazene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): D.P.C. is named as inventor on a patent application related to polyphosphazene nanoparticles and holds stock in a company, PolyAurum, that is developing gold nanoparticles for biological applications.
Figures


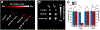

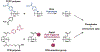
References
-
- Moloney JN; Cotter TG ROS signalling in the Biology of Cancer. Semin.Cell Dev. Biol 2018, 80, 50–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

