Evolution from Covalent to Self-Assembled PAMAM-Based Dendrimers as Nanovectors for siRNA Delivery in Cancer by Coupled In Silico-Experimental Studies. Part I: Covalent siRNA Nanocarriers
- PMID: 31323863
- PMCID: PMC6680565
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11070351
Evolution from Covalent to Self-Assembled PAMAM-Based Dendrimers as Nanovectors for siRNA Delivery in Cancer by Coupled In Silico-Experimental Studies. Part I: Covalent siRNA Nanocarriers
Abstract
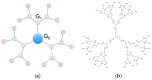
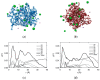
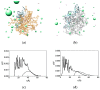
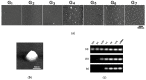
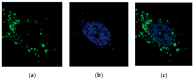
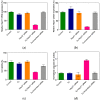
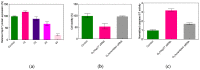
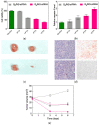
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) represent a new approach towards the inhibition of gene expression; as such, they have rapidly emerged as promising therapeutics for a plethora of important human pathologies including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and other disorders of a genetic etiology. However, the clinical translation of RNA interference (RNAi) requires safe and efficient vectors for siRNA delivery into cells. Dendrimers are attractive nanovectors to serve this purpose, as they present a unique, well-defined architecture and exhibit cooperative and multivalent effects at the nanoscale. This short review presents a brief introduction to RNAi-based therapeutics, the advantages offered by dendrimers as siRNA nanocarriers, and the remarkable results we achieved with bio-inspired, structurally flexible covalent dendrimers. In the companion paper, we next report our recent efforts in designing, characterizing and testing a series of self-assembled amphiphilic dendrimers and their related structural alterations to achieve unprecedented efficient siRNA delivery both in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: PAMAM dendrimers; RNAi therapeutics; covalent dendrimers; gene silencing; nanovectors; siRNA delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

