Induction of Acquired Resistance towards EGFR Inhibitor Gefitinib in a Patient-Derived Xenograft Model of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Subsequent Molecular Characterization
- PMID: 31323891
- PMCID: PMC6678194
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8070740
Induction of Acquired Resistance towards EGFR Inhibitor Gefitinib in a Patient-Derived Xenograft Model of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Subsequent Molecular Characterization
Abstract
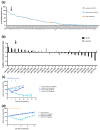
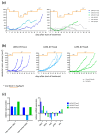
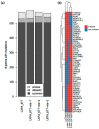
In up to 30% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, the oncogenic driver of tumor growth is a constitutively activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Although these patients gain great benefit from treatment with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, the development of resistance is inevitable. To model the emergence of drug resistance, an EGFR-driven, patient-derived xenograft (PDX) NSCLC model was treated continuously with Gefitinib in vivo. Over a period of more than three months, three separate clones developed and were subsequently analyzed: Whole exome sequencing and reverse phase protein arrays (RPPAs) were performed to identify the mechanism of resistance. In total, 13 genes were identified, which were mutated in all three resistant lines. Amongst them the mutations in NOMO2, ARHGEF5 and SMTNL2 were predicted as deleterious. The 53 mutated genes specific for at least two of the resistant lines were mainly involved in cell cycle activities or the Fanconi anemia pathway. On a protein level, total EGFR, total Axl, phospho-NFκB, and phospho-Stat1 were upregulated. Stat1, Stat3, MEK1/2, and NFκB displayed enhanced activation in the resistant clones determined by the phosphorylated vs. total protein ratio. In summary, we developed an NSCLC PDX line modelling possible escape mechanism under EGFR treatment. We identified three genes that have not been described before to be involved in an acquired EGFR resistance. Further functional studies are needed to decipher the underlying pathway regulation.
Keywords: EGFR inhibition; NSCLC; PDX; acquired resistance; reverse phase protein array; whole exome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ELK1/MTOR/S6K1 Pathway Contributes to Acquired Resistance to Gefitinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 17;25(4):2382. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042382. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38397056 Free PMC article.
-
A novel STAT3 inhibitor W2014-S regresses human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts and sensitizes EGFR-TKI acquired resistance.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(2):824-840. doi: 10.7150/thno.49600. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391507 Free PMC article.
-
miR-762 activation confers acquired resistance to gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2019 Dec 10;19(1):1203. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6416-4. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31823748 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C131-C137. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200613. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230005 Review.
Cited by
-
Triptolide inhibits epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and induces apoptosis in gefitinib‑resistant lung cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2020 May;43(5):1569-1579. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7542. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32323848 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-derived xenograft models in cancer therapy: technologies and applications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Apr 12;8(1):160. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01419-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37045827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Footprints: Stamping hallmarks of lung cancer with patient-derived models, from molecular mechanisms to clinical translation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 21;11:1132940. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1132940. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36911198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zebrafish patient-derived xenograft models predict lymph node involvement and treatment outcome in non-small cell lung cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Feb 9;41(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02280-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35139880 Free PMC article.
-
Generation, evolution, interfering factors, applications, and challenges of patient-derived xenograft models in immunodeficient mice.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Jun 21;23(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02953-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37344821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang Z. ErbB Receptors and Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017;1652:3–35. - PubMed
-
- Siu M.K., Abou-Kheir W., Yin J.J., Chang Y.S., Barrett B., Suau F., Casey O., Chen W.Y., Fang L., Hynes P., et al. Loss of EGFR signaling regulated miR-203 promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis and tyrosine kinase inhibitors resistance. Oncotarget. 2014;5:3770–3784. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1994. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

