Hybrid Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective Determination of Methamphetamine and Amphetamine in Dyed Hair by Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 31323938
- PMCID: PMC6651873
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24132501
Hybrid Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective Determination of Methamphetamine and Amphetamine in Dyed Hair by Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
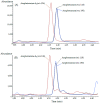
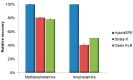
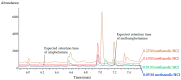
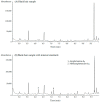
Sample preparation is an important step in the isolation of target compounds from complex matrices to perform their reliable and accurate analysis. Hair samples are commonly pulverized or processed as fine cut, depending on preference, before extraction by techniques such as solid-phase extraction (SPE), liquid-liquid extraction, and other methods. In this study, a method based on hybrid solid-phase extraction (hybridSPE) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was developed and validated for the determination of methamphetamine (MA) and amphetamine (AP) in hair. The hair samples were mechanically pulverized after washing with de-ionized water and acetone. The samples were then sonicated in methanol at 50 °C for 1 h and centrifuged at 50,000× g for 3 min. The supernatants were transferred onto the hybridSPE cartridge and extracted using 1 mL of 0.05 M methanolic hydrogen chloride. The combined solutions were evaporated to dryness, derivatized using pentafluoropropionic anhydride, and analyzed by GC-MS. Excellent linearity (R2 > 0.9998) was achieved in the ranges of 0.05-5.0 ng/mg for AP and 0.1-10.0 ng/mg for MA. The recovery was 83.4-96.8%. The intra- and inter-day accuracies were -9.4% to 5.5% and -5.1% to 3.1%, while the intra- and inter-day precisions were within 8.3% and 6.7%, respectively. The limits of detections were 0.016 ng/mg for AP and 0.031 ng/mg for MA. The validated hybridSPE method was applied to dyed hair for MA and AP extraction and compared to a methanol extraction method currently being used in our laboratory. The results showed that an additional hybridSPE step improved the recovery by 5.7% for low-concentration quality control (QC) samples and by 24.1% for high-concentration QC samples. Additionally, the hybridSPE method was compared to polymeric reversed-phase SPE methods, and the absolute recoveries for hybridSPE were 50% and 20% greater for AP (1.5 ng/mg) and MA (3.0 ng/mg), respectively. In short, the hybridSPE technique was shown to minimize the matrix effects, improving GC-MS analysis of hair. Based on the results, the proposed method proved to be effective for the selective determination of MA and AP in hair samples.
Keywords: GC–MS; amphetamine; hair analysis; hybridSPE; methamphetamine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: “Methamphetamine Continues to Dominate Synthetic Drug Markets”, Global Smart Update Volume 20, August 2018. [(accessed on 15 May 2019)]; Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Global_Smart_Update_20_web.pdf.
-
- Ando E., Hayashida M., Nihira M., Yamada T., Ohno Y. GC-MS analysis of methamphetamine and amphetamine in hair of Thai drug addicts. J. Alcohol Stud. Drug Depend. 2004;39:168–179. - PubMed
-
- Supreme Prosecutors’ Office: 2017 White Paper on Drug-Related Crimes. [(accessed on 15 May 2019)]; Available online: http://antidrug.drugfree.or.kr/page/?mIdx=190&mode=view&idx=12433&retUrl....
-
- Supreme Prosecutors’ Office: 2016 White Paper on Drug-Related Crimes. [(accessed on 15 May 2019)]; Available online: http://antidrug.drugfree.or.kr/page/?mIdx=190&mode=view&idx=10839&retUrl....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

