(R)-Ketamine Induces a Greater Increase in Prefrontal 5-HT Release Than (S)-Ketamine and Ketamine Metabolites via an AMPA Receptor-Independent Mechanism
- PMID: 31325908
- PMCID: PMC6822138
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyz041
(R)-Ketamine Induces a Greater Increase in Prefrontal 5-HT Release Than (S)-Ketamine and Ketamine Metabolites via an AMPA Receptor-Independent Mechanism
Abstract
Background: Although recent studies provide insight into the molecular mechanisms of the effects of ketamine, the antidepressant mechanism of ketamine enantiomers and their metabolites is not fully understood. In view of the involvement of mechanisms other than the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in ketamine's action, we investigated the effects of (R)-ketamine, (S)-ketamine, (R)-norketamine [(R)-NK], (S)-NK, (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine [(2R,6R)-HNK], and (2S,6S)-HNK on monoaminergic neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex of mice.
Methods: The extracellular monoamine levels in the prefrontal cortex were measured by in vivo microdialysis.
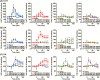
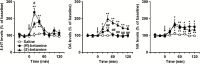
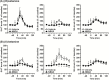
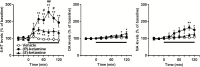
Results: (R)-Ketamine and (S)-ketamine acutely increased serotonin release in a dose-dependent manner, and the effect of (R)-ketamine was greater than that of (S)-ketamine. In contrast, (S)-ketamine caused a robust increase in dopamine release compared with (R)-ketamine. Both ketamine enantiomers increased noradrenaline release, but these effects did not differ. (2R,6R)-HNK caused a slight but significant increase in serotonin and noradrenaline but not dopamine release. (S)-NK increased dopamine and noradrenaline but not serotonin release. Differential effects between (R)-ketamine and (S)-ketamine were also observed in a lipopolysaccharide-induced model of depression. An α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor antagonist, 2,3-dioxo-6-nitro-1,2,3,4- tetrahydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide (NBQX), attenuated (S)-ketamine-induced, but not (R)-ketamine-induced serotonin release, whereas NBQX blocked dopamine release induced by both enantiomers. Local application of (R)-ketamine into the prefrontal cortex caused a greater increase in prefrontal serotonin release than that of (S)-ketamine.
Conclusions: (R)-Ketamine strongly activates the prefrontal serotonergic system through an AMPA receptor-independent mechanism. (S)-Ketamine-induced serotonin and dopamine release was AMPA receptor-dependent. These findings provide a neurochemical basis for the underlying pharmacological differences between ketamine enantiomers and their metabolites.
Keywords: (R)-ketamine; (S)-ketamine; AMPA receptors; monoamine; prefrontal cortex.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures
References
-
- Ago Y, Nakamura S, Baba A, Matsuda T (2005) Sulpiride in combination with fluvoxamine increases in vivo dopamine release selectively in rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Ago Y, Hasebe S, Hiramatsu N, Hashimoto H, Takuma K, Matsuda T (2017) Psychopharmacology of combined activation of the serotonin1a and σ1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 809:172–177. - PubMed
-
- Araki R, Ago Y, Hasebe S, Nishiyama S, Tanaka T, Oka S, Takuma K, Matsuda T (2014) Involvement of prefrontal AMPA receptors in encounter stimulation-induced hyperactivity in isolation-reared mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:883–893. - PubMed
-
- Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, Krystal JH (2000) Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:351–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

