Impact of Immune System Activation and Vascular Impairment on Male and Female Sexual Dysfunction
- PMID: 31326360
- PMCID: PMC6773509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2019.05.005
Impact of Immune System Activation and Vascular Impairment on Male and Female Sexual Dysfunction
Abstract
Introduction: Male and female sexual dysfunction (SD) is considered a multifactorial condition. Numerous studies have shown the involvement of inflammatory processes in this pathological condition. Sexual intercourse requires healthy and functioning vessels to supply the pelvic region in both males and females, generating penile erection and clitoral and vaginal lubrication, respectively. Cardiovascular diseases and associated risk factors may contribute negatively to pelvic blood flow, possibly through immune system activation.
Aim: The study aimed to address the correlation between vascular inflammation driven by immune system activation and SD in males and females.
Methods: A literature review was performed to identify articles addressing male and female SD and vascular inflammation. Key words included "male and female sexual dysfunction," "vascular inflammation," "iliac and pudendal arteries dysfunction," "genitourinary tract," and "blood flow."
Main outcome measures: Management of systemic and local inflammation may be a useful alternative to improve SD and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases in the future.
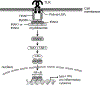
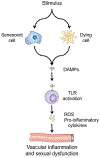
Results: Increased levels of cytokines and chemokines have been detected in humans and animals with hypertension, obesity, and diabetic conditions. Chronic activation of the innate immune system, especially by pathogen- or damage-associated molecular patterns, and metabolic-related disorders may act as triggers further contributing to an increased inflammatory condition. Due to the reduced size of vessels, SD and retinal vascular impairments have been shown to be predictive factors for cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, considering that blood flow to the genitalia is essential for sexual function, endothelial dysfunction and vascular remodeling, secondary to chronic immune system activation, may be implicated in male and female vasculogenic SD.
Conclusions: Several conditions appear to play a role in SD. In the present review, we have identified a role for the immune system in generating vascular and tissue impairments contributing to erectile dysfunction and female SD. Calmasini FB, Klee N, Webb RC, et al. Impact of Immune System Activation and Vascular Impairment on Male and Female Sexual Dysfunction. Sex Med Rev 2019;7:604-613.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Endothelial dysfunction; Erectile dysfunction; Female sexual dysfunction; Innate immune system; Vascular inflammation.
Copyright © 2019 International Society for Sexual Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cardiometabolic Risk and Female Sexuality-Part I. Risk Factors and Potential Pathophysiological Underpinnings for Female Vasculogenic Sexual Dysfunction Syndromes.Sex Med Rev. 2018 Oct;6(4):508-524. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 May 2. Sex Med Rev. 2018. PMID: 29730315 Review.
-
[Relation between sexual dysfunction and metabolic syndrome].Orv Hetil. 2019 Jan;160(3):98-103. doi: 10.1556/650.2019.31235. Orv Hetil. 2019. PMID: 30640528 Hungarian.
-
Sexual dysfunction with aging and systemic hypertension.Am J Cardiol. 1988 Jun 15;61(16):18H-23H. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(88)91100-9. Am J Cardiol. 1988. PMID: 3289346 Review.
-
Cardiometabolic Diseases and Female Sexual Dysfunction: Animal Studies.J Sex Med. 2022 Mar;19(3):408-420. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2021.12.009. Epub 2022 Jan 19. J Sex Med. 2022. PMID: 35063393 Review.
-
Vasculogenic female sexual dysfunction: vaginal engorgement and clitoral erectile insufficiency syndromes.Int J Impot Res. 1998 May;10 Suppl 2:S84-90; discussion S98-101. Int J Impot Res. 1998. PMID: 9647967 Review.
Cited by
-
Causal relationship between immune cells, inflammatory cytokines, metabolites, and erectile dysfunction: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Transl Androl Urol. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):2448-2458. doi: 10.21037/tau-24-395. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Transl Androl Urol. 2024. PMID: 39698561 Free PMC article.
-
Causal associations of psoriasis with male sexual and reproductive health: a univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Aug 16;316(8):522. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03280-x. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39150584 No abstract available.
-
Biology of iatrogenic sexual dysfunction in men and women survivors of cancer.Urol Oncol. 2022 Aug;40(8):366-371. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2021.01.017. Epub 2021 Feb 7. Urol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 33563538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Gas: A Novel Type of Antioxidant in Modulating Sexual Organs Homeostasis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jan 16;2021:8844346. doi: 10.1155/2021/8844346. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33510842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A causal link between circulating immune cells and erectile dysfunction: Two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 27;103(52):e41124. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041124. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39969333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lotti F, Maggi M. Sexual dysfunction and male infertility. Nat Rev Urol 2018;15(5):287–307. - PubMed
-
- Lewis RW, Fugl-Meyer KS, Corona G, et al. Definitions/epidemiology/risk factors for sexual dysfunction. J Sex Med 2010;7(4 Pt 2):1598–607. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues FL, Fais RS, Tostes RC et al. There is a link between erectile dysfunction and heart failure: it could be inflammation. Curr Drug Target 2015; 16(5):442–450. - PubMed
-
- Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Giugliano D, et al. From inflammation to sexual dysfunctions: a journey through diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest 2018; 41(11):1249–1258. - PubMed
-
- Puppo V, Puppo G. Anatomy of sex: Revision of the new anatomical terms used for the clitoris and the female orgasm by sexologists. Clin Anat 2015;28(3):293–304. - PubMed

