Short-course primaquine for the radical cure of Plasmodium vivax malaria: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled non-inferiority trial
- PMID: 31327563
- PMCID: PMC6753019
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31285-1
Short-course primaquine for the radical cure of Plasmodium vivax malaria: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled non-inferiority trial
Abstract
Background: Primaquine is the only widely used drug that prevents Plasmodium vivax malaria relapses, but adherence to the standard 14-day regimen is poor. We aimed to assess the efficacy of a shorter course (7 days) of primaquine for radical cure of vivax malaria.
Methods: We did a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, non-inferiority trial in eight health-care clinics (two each in Afghanistan, Ethiopia, Indonesia, and Vietnam). Patients (aged ≥6 months) with normal glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) and presenting with uncomplicated vivax malaria were enrolled. Patients were given standard blood schizontocidal treatment and randomly assigned (2:2:1) to receive 7 days of supervised primaquine (1·0 mg/kg per day), 14 days of supervised primaquine (0·5 mg/kg per day), or placebo. The primary endpoint was the incidence rate of symptomatic P vivax parasitaemia during the 12-month follow-up period, assessed in the intention-to-treat population. A margin of 0·07 recurrences per person-year was used to establish non-inferiority of the 7-day regimen compared with the 14-day regimen. This trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01814683).
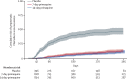
Findings: Between July 20, 2014, and Nov 25, 2017, 2336 patients were enrolled. The incidence rate of symptomatic recurrent P vivax malaria was 0·18 (95% CI 0·15 to 0·21) recurrences per person-year for 935 patients in the 7-day primaquine group and 0·16 (0·13 to 0·18) for 937 patients in the 14-day primaquine group, a difference of 0·02 (-0·02 to 0·05, p=0·3405). The incidence rate for 464 patients in the placebo group was 0·96 (95% CI 0·83 to 1·08) recurrences per person-year. Potentially drug-related serious adverse events within 42 days of starting treatment were reported in nine (1·0%) of 935 patients in the 7-day group, one (0·1%) of 937 in the 14-day group and none of 464 in the control arm. Four of the serious adverse events were significant haemolysis (three in the 7-day group and one in the 14-day group).
Interpretation: In patients with normal G6PD, 7-day primaquine was well tolerated and non-inferior to 14-day primaquine. The short-course regimen might improve adherence and therefore the effectiveness of primaquine for radical cure of P vivax malaria.
Funding: UK Department for International Development, UK Medical Research Council, UK National Institute for Health Research, and the Wellcome Trust through the Joint Global Health Trials Scheme (MR/K007424/1) and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (OPP1054404).
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
A shorter course for anti-relapse therapy against vivax malaria.Lancet. 2019 Sep 14;394(10202):898-900. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31605-8. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31327565 No abstract available.
-
Primaquine for Plasmodium vivax malaria treatment.Lancet. 2020 Jun 27;395(10242):1971-1972. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30242-7. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32593332 No abstract available.
References
-
- Battle KE, Gething PW, Elyazar IR. The global public health significance of Plasmodium vivax. Adv Parasitol. 2012;80:1–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous