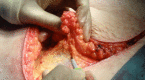
The use of plasmakinetic cautery compared to conventional electrocautery for dissection of abdominal free flap for breast reconstruction: single-centre, randomized controlled study
- PMID: 31328103
- PMCID: PMC6606469
- DOI: 10.21037/gs.2018.12.04
The use of plasmakinetic cautery compared to conventional electrocautery for dissection of abdominal free flap for breast reconstruction: single-centre, randomized controlled study
Abstract
Background: The plasmakinetic cautery is a surgical dissection instrument that combines scalpel-like cutting precision with electrocautery-like haemostasis properties, and operates at lower temperatures (40-170 °C) than conventional electrocautery (200-350 °C). The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical benefits of using plasmakinetic cautery in abdominal free flap dissection for breast reconstruction.
Methods: Forty women undergoing abdominal-based microsurgical breast reconstruction (DIEP/MS-TRAM) were randomized to plasmakinetic cautery (n=20) or conventional electrocautery (n=20) for dissection of the abdominal free flap. Total abdominal wound drainage volume/duration, operation time and complications such as seroma and haematoma were examined.
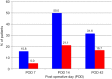
Results: Age, body mass index, type of reconstruction and abdominal flap weight were similar in both groups. Mean abdominal drainage volume was (279±262) mL in conventional electrocautery group and (294±265) mL in plasmakinetic cautery group (P=0.853). Plasmakinetic cautery group mean drainage duration (4.3±2.2 days) was no difference compared to conventional diathermy group (3.8±2.0 days, P=0.501). Mean operation time in the conventional electrocautery group and plasmakinetic cautery group was 157±50 vs. 174±70 min respectively (P=0.195). There was more seroma detected in the conventional electrocautery group compared to plasmakinetic cautery group at days 7, 14 and 42 post-operation, but this was not statically significant. 2 haematomas in conventional diathermy group and 1 haematoms in the plasmakinetic cautery group required evacuation.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that there are no significant differences between the use of plasmakinetic cautery and conventional electrocautery for abdominal free flap dissection.
Keywords: Breast reconstruction; abdominal flap dissection; breast reconstruction complications; peak plasmablade; plasmakinetic cautery; seroma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of plasmakinetic cautery on wound healing and complications in mastectomy.J Breast Cancer. 2013 Jun;16(2):198-201. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2013.16.2.198. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Breast Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23843853 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of two different electrosurgical devices in reduction mammoplasty: Monopolar electrocautery versus plasmakinetic cautery.World J Surg. 2024 Aug;48(8):1929-1933. doi: 10.1002/wjs.12259. Epub 2024 Jun 24. World J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38924600 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing the Harmonic Scalpel with Electrocautery in Reducing Postoperative Flap Necrosis and Seroma Formation after Modified Radical Mastectomy in Carcinoma Breast Patients: A Double-Blind Prospective Randomized Control Trail.Cureus. 2018 Apr 13;10(4):e2476. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2476. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 29904617 Free PMC article.
-
Harmonic scalpels compared with electrocautery in reconstructive flap harvesting: A meta-analysis.Microsurgery. 2022 Jan;42(1):89-96. doi: 10.1002/micr.30831. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Microsurgery. 2022. PMID: 34652038 Review.
-
Abdominal wall following free TRAM or DIEP flap reconstruction: a meta-analysis and critical review.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009 Sep;124(3):752-764. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31818b7533. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009. PMID: 19342994 Review.
Cited by
-
Similarity of Seroma Rate at the Medial Thigh following Free Flap Harvesting or Medial Thigh Lift: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JPRAS Open. 2024 Apr 5;40:360-374. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2024.03.013. eCollection 2024 Jun. JPRAS Open. 2024. PMID: 38770115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smoke analysis of a new surgical system that applies low-temperature plasma.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Oct;10(19):1053. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-608. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36330412 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Seroma Formation at the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator, Transverse Musculocutaneous Gracilis, and Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flap Donor Sites after Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction.Arch Plast Surg. 2022 Jul 30;49(4):494-500. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1751103. eCollection 2022 Jul. Arch Plast Surg. 2022. PMID: 35919555 Free PMC article.
-
PlasmaBlade versus Electrocautery for Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Harvesting in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: A Comparative Clinical Outcome Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 19;13(8):2388. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082388. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cancer Research UK. Breast cancer incidence statistics. 2014; Available online: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/st.... Accessed April 5, 2016.
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellent. NICE guidance2009. Early and locally advanced breast cancer: diagnosis and treatment. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG80/chapter/1-Guidance#breast-reconstr.... Accessed April 5, 2016.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources