BI-RADS 4 breast lesions: could multi-mode ultrasound be helpful for their diagnosis?
- PMID: 31328105
- PMCID: PMC6606479
- DOI: 10.21037/gs.2019.05.01
BI-RADS 4 breast lesions: could multi-mode ultrasound be helpful for their diagnosis?
Abstract
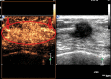
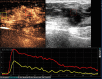
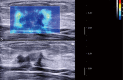
Background: The malignant probability of Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 4 breast lesions is 3-94%, which is a very large span, and thus leads to a high rate of unnecessary biopsy. Therefore, the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant BI-RADS 4 breast lesions has become extremely important. Thus, in this paper, we investigated the diagnostic value of conventional ultrasonography (US), contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and shear wave elastography (SWE) for BI-RADS 4 breast lesions, and tried to figure out a multi-mode ultrasonic method for them.
Methods: From March 2016 to May 2017, 118 breast lesions that were categorized as BI-RADS 4 lesions by US were studied with CEUS and SWE. All the lesions were confirmed by pathology via surgery or vacuum-assisted biopsy. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of US, CEUS and SWE were analyzed. Then the diagnostic efficacies of US, CEUS, SWE and the combination of these modalities were compared. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the independent risk factors. A multi-mode method to evaluate BI-RADS 4 lesions based on the logistic regression was developed.
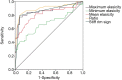
Results: Of the 118 BI-RADS 4 lesions, 74 lesions (62.7%) were benign and 44 lesions (37.3%) were malignant. The diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for US, US + CEUS, US + SWE, US + CEUS + SWE were 88.6% and 75.7%, 86.4% and 94.6%, 88.6% and 90.5%, 97.7% and 93.2%, respectively. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of US + SWE + CEUS was significantly higher than that of US (P<0.0001), US + CEUS (P=0.020), but there was no significant difference between the AUC of US + SWE + CEUS and the AUC of US + SWE.
Conclusions: US + CEUS + SWE and US + SWE could significantly improve the diagnostic efficiency and accuracy of US in the diagnosis of BI-RADS 4 breast lesions.
Keywords: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS); Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS); breast lesions; shear wave elastography (SWE).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The application of multimodal ultrasound examination in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions of BI-RADS category 4.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 9;12:1596100. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1596100. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40552183 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant BI-RADS 4 Breast Masses by Contrastenhanced Ultrasound Combined with Shear Wave Elastography.Curr Med Imaging. 2023 Oct 31. doi: 10.2174/0115734056257195231025072821. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37921152
-
Evaluation of diagnostic efficacy of multimode ultrasound in BI-RADS 4 breast neoplasms and establishment of a predictive model.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 24;12:1053280. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1053280. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36505867 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and Shear Wave Elastography in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Lesions: A Network Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2019 Mar 5;9:102. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00102. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30891425 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and superb microvascular imaging in differentiating benign from malignant solid breast lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2022;81(2):109-121. doi: 10.3233/CH-211367. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2022. PMID: 35180108
Cited by
-
Shear-wave elastography combined with contrast-enhanced ultrasound algorithm for noninvasive characterization of focal liver lesions.Radiol Med. 2023 Jan;128(1):6-15. doi: 10.1007/s11547-022-01575-5. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Radiol Med. 2023. PMID: 36525179
-
Breast tumor diagnosis via multimodal deep learning using ultrasound B-mode and Nakagami images.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2025 Nov;12(Suppl 2):S22009. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.12.S2.S22009. Epub 2025 May 14. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2025. PMID: 40375887
-
A clinical-radiomics nomogram based on multimodal ultrasound for predicting the malignancy risk in solid hypoechoic breast lesions.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 17;13:1256146. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1256146. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37916158 Free PMC article.
-
Non-mass Breast Lesions: Could Multimodal Ultrasound Imaging Be Helpful for Their Diagnosis?Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;12(12):2923. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12122923. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552930 Free PMC article.
-
The Accuracy of Breast Cancer Diagnostic Tools.Cureus. 2024 Jan 7;16(1):e51776. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51776. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38192524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spak DA, Plaxco JS, Santiago L, et al. BI-RADS((R)) fifth edition: A summary of changes. Diagn Interv Imaging 2017;98:179-90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
