Vitamin D and Phenylbutyrate Supplementation Does Not Modulate Gut Derived Immune Activation in HIV-1
- PMID: 31330899
- PMCID: PMC6682943
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11071675
Vitamin D and Phenylbutyrate Supplementation Does Not Modulate Gut Derived Immune Activation in HIV-1
Abstract
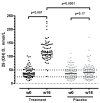
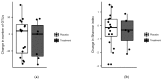
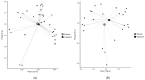
Dysbiosis and a dysregulated gut immune barrier function contributes to chronic immune activation in HIV-1 infection. We investigated if nutritional supplementation with vitamin D and phenylbutyrate could improve gut-derived inflammation, selected microbial metabolites, and composition of the gut microbiota. Treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected individuals (n = 167) were included from a double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled trial of daily 5000 IU vitamin D and 500 mg phenylbutyrate for 16 weeks (Clinicaltrials.gov NCT01702974). Baseline and per-protocol plasma samples at week 16 were analysed for soluble CD14, the antimicrobial peptide LL-37, kynurenine/tryptophan-ratio, TMAO, choline, and betaine. Assessment of the gut microbiota involved 16S rRNA gene sequencing of colonic biopsies. Vitamin D + phenylbutyrate treatment significantly increased 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (p < 0.001) but had no effects on sCD14, the kynurenine/tryptophan-ratio, TMAO, or choline levels. Subgroup-analyses of vitamin D insufficient subjects demonstrated a significant increase of LL-37 in the treatment group (p = 0.02), whereas treatment failed to significantly impact LL-37-levels in multiple regression analysis. Further, no effects on the microbiota was found in number of operational taxonomic units (p = 0.71), Shannon microbial diversity index (p = 0.82), or in principal component analyses (p = 0.83). Nutritional supplementation with vitamin D + phenylbutyrate did not modulate gut-derived inflammatory markers or microbial composition in treatment-naïve HIV-1 individuals with active viral replication.
Keywords: HIV-1; LL-37; TMAO; clinical trial; kynurenine/tryptophan ratio; microbiota; phenylbutyrate; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Vujkovic-Cvijin I., Dunham R.M., Iwai S., Maher M.C., Albright R.G., Broadhurst M.J., Hernandez R.D., Lederman M.M., Huang Y., Somsouk M., et al. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota is associated with hiv disease progression and tryptophan catabolism. Sci. Trans. Med. 2013;5:193ra191. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006438. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vazquez-Castellanos J.F., Serrano-Villar S., Latorre A., Artacho A., Ferrus M.L., Madrid N., Vallejo A., Sainz T., Martinez-Botas J., Ferrando-Martinez S., et al. Altered metabolism of gut microbiota contributes to chronic immune activation in HIV-infected individuals. Mucosal Immunol. 2015;8:760–772. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.107. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Qi Q., Hua S., Clish C.B., Scott J.M., Hanna D.B., Wang T., Haberlen S.A., Shah S.J., Glesby M.J., Lazar J.M., et al. Plasma tryptophan-kynurenine metabolites are altered in HIV infection and associated with progression of carotid artery atherosclerosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018;67:235–242. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

