Five-year follow-up of SWOG S0816: limitations and values of a PET-adapted approach with stage III/IV Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 31331918
- PMCID: PMC6788007
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019000719
Five-year follow-up of SWOG S0816: limitations and values of a PET-adapted approach with stage III/IV Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
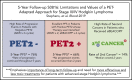
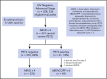
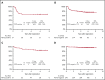
Patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) demonstrated excellent 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) after receiving positron emission tomography (PET)-adapted therapy on SWOG S0816. Patients received 2 cycles of doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD). Patients achieving complete response (CR) on PET scan following cycle 2 of ABVD (PET2) continued 4 additional cycles of ABVD. Patients not achieving CR on PET2 were switched to escalated bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone (eBEACOPP) for 6 cycles. After a median follow-up of 5.9 years, a subset of 331 eligible patients with central review of PET2 was analyzed. PET2 was negative in 82% and positive in 18%. For all patients, the estimated 5-year PFS and OS was 74% (95% confidence interval [CI], 69%-79%) and 94% (95% CI, 91%-96%), respectively. For PET2- and PET2+ patients, the 5-year PFS was 76% (95% CI, 70%-81%) and 66% (95% CI, 52%-76%), respectively. Seven (14%) and 6 (2%) patients reported second cancers after treatment with eBEACOPP and ABVD, respectively (P = .001). Long-term OS of HL patients treated on S0816 remains high. Nearly 25% of PET2- patients experienced relapse events, demonstrating limitations ABVD therapy and of the negative predictive value of PET2. In PET2+ patients who received eBEACOPP, PFS was favorable, but was associated with a high rate of second malignancies compared with historical controls. Our results emphasize the importance of long-term follow-up, and the need for more efficacious and less toxic therapeutic approaches for advanced-stage HL patients. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT00822120.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: D.M.S. has received research funding from Acerta, Gilead, Karyopharm and honoraria from Genentech. H.S. has served as a consultant for Allero Therapeutics. D.J.S. has received research funding from and serves as a consultant for Seattle Genetics. L.M.R. holds a patent through NanoString. N.L.B. has received research funding from Gilead, Kite, Seattle Genetics, Affimed, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Forty Seven, Genentech, Immune Design, Janssen, Merck, Millennium, and Pharmacyclics, and serves as a consultant for Pfizer and Acerta. A.M.E. serves as a consultant for and has received honoraria from Seattle Genetics, Bayer, Verastem, and Pharmacyclics. A.S.L. serves as a consultant for Seattle Genetics and Bristol-Myers Squibb. P.M.B. serves as a consultant for AbbVie. E.D.H. serves as a consultant for Celgene, Seattle Genetics, and Jazz and has received research funding from AbbVie and Eli Lilly. J.P.L. serves as a consultant for Celgene, Juno, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sutro, Gilead, Genentech, Pfizer, Bayer, Biotest, United Therapeutics, Karyopharm, ADC Therapeutics, MEI Pharma, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. B.S.K. serves as a consultant for Genentech, Celgene, Acerta, AstraZeneca, Juno, CTI, ADC Therapeutics, AbbVie, Gilead, and Seattle Genetics. S.M.S. serves as a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Humanigen, and Seattle Genetics and has received research funding from Forty Seven and Sanofi. J.W.F. has received honoraria from Bayer. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
PET-adapted treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma.Blood. 2019 Oct 10;134(15):1200-1201. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002420. Blood. 2019. PMID: 31698414 No abstract available.
-
Interim PET Assessment of Advanced Hodgkin Lymphoma: Is It Sufficient?J Nucl Med. 2020 Nov;61(11):1694-1695. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.242594. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32060220 No abstract available.
-
Reply: Interim PET Assessment of Advanced Hodgkin Lymphoma: Is It Sufficient?J Nucl Med. 2020 Nov;61(11):1695. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.242685. Epub 2020 Sep 11. J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32917781 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Duggan DB, Petroni GR, Johnson JL, et al. Randomized comparison of ABVD and MOPP/ABV hybrid for the treatment of advanced Hodgkin’s disease: report of an intergroup trial. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(4):607-614. - PubMed
-
- Gordon LI, Hong F, Fisher RI, et al. Randomized phase III trial of ABVD versus Stanford V with or without radiation therapy in locally extensive and advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma: an intergroup study coordinated by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (E2496). J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(6):684-691. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sieniawski M, Reineke T, Nogova L, et al. Fertility in male patients with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma treated with BEACOPP: a report of the German Hodgkin Study Group (GHSG). Blood. 2008;111(1):71-76. - PubMed
-
- Engert A, Diehl V, Franklin J, et al. Escalated-dose BEACOPP in the treatment of patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma: 10 years of follow-up of the GHSG HD9 study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(27):4548-4554. - PubMed
-
- Borchmann P, Haverkamp H, Lohri A, et al. Progression-free survival of early interim PET-positive patients with advanced stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma treated with BEACOPPescalated alone or in combination with rituximab (HD18): an open-label, international, randomised phase 3 study by the German Hodgkin Study Group. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(4):454-463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233290/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180818/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233339/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180833/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA180803/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

