The Genetic Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes: Opportunities for Health Translation
- PMID: 31332628
- PMCID: PMC8059416
- DOI: 10.1007/s11892-019-1173-y
The Genetic Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes: Opportunities for Health Translation
Abstract
Purpose of review: Genome-wide association studies have delineated the genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes. While functional studies to identify target transcripts are ongoing, new genetic knowledge can be translated directly to health applications. The review covers several translation directions but focuses on genomic polygenic scores for screening and prevention.
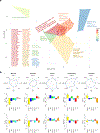
Recent findings: Over 400 genomic variants associated with T2D and its related quantitative traits are now known. Genetic scores comprising dozens to millions of associated variants can predict incident T2D. However, measurement of body mass index is more efficient than genetic scores to detect T2D risk groups, and knowledge of T2D genetic risk alone seems insufficient to improve health. Genetically determined metabolic sub-phenotypes can be identified by clustering variants associated with physiological axes like insulin resistance. Genetic sub-phenotyping may be a way forward to identify specific individual phenotypes for prevention and treatment. Genomic polygenic scores for T2D can predict incident diabetes but may not be useful to improve health overall. Genetic detection of T2D sub-phenotypes could be useful to personalize screening and care.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Genetics; Genomics; Health outcomes; Risk score; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Figures
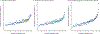

References
-
- Florez JC, Udler MS, Hanson RL. Genetics of type 2 diabetes. In: Cowie CCCS, Menke A, Cissell MA, Eberhardt MS, Meigs JB, Gregg EW, Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Becker DJ, Brancati FL, Boyko EJ, Herman WH, Howard BV, Narayan KMV, Rewers M, Fradkin JE, editors. Diabetes in America, 3rd ed NIH Pub No. 17–1468 ed. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health; 2018. p. 14.1–25.
-
-
Mahajan A, Taliun D, Thurner M, Robertson NR, Torres JM, Rayner NW, et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat Genet. 2018;50(11):1505–13
•• This genome-wide association study of more than one million people of European ancestry is the current “definitive” framework for T2D common variant genetic architecture. Supplementary Figure 10 shows the distribution of a genomic polygenic score for T2D in individuals of European ancestry.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

