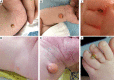
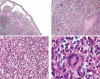
Congenital multiple juvenile xanthogranuloma
- PMID: 31333355
- PMCID: PMC6640009
- DOI: 10.5114/ada.2019.85643
Congenital multiple juvenile xanthogranuloma
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adamson NF. Congenital xanthoma multiplex in a child. Br J Dermatol. 1905;17:222–3.
-
- McDonagh JER. A contribution to our knowledge of the naevo-xantho-endothelioma. Br J Dermat. 1912;24:85.
-
- Helwig EB, Hackney VC. Juvenile xanthogranuloma (nevoxanthoendothelioma) Am J Path. 1954;30:365.
-
- Dehner LP. Juvenile xanthogranuloma in the first decades of life. A clinicopathologic study of 174 cases with cutaneous an extracutaneous manifestations. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:579–93. - PubMed
-
- Curtis T, Wheeler DT, Cibis GW, et al. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. Available at: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1209681-overview.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
