Management of traumatic flail chest in intensive care unit: An experience from trauma center ICU
- PMID: 31333360
- PMCID: PMC6625290
- DOI: 10.4103/sja.SJA_699_18
Management of traumatic flail chest in intensive care unit: An experience from trauma center ICU
Abstract
Background/aim: The thoracic injury and related complications are responsible for upto 25% of blunt trauma mortality. This study is designed to compare these two popular ventilation modes in traumatic flail chest.
Materials and method: A total of 30 patients with thoracic trauma, aged 18-60 years, were enrolled in this study for a period of 1 year. The Thoracic Trauma Severity Score (TTSS) was used for assessing the severity of chest injury. Patients were divided into two treatment groups: one recieved endotracheal intubation with mechanical ventilation (ET group, n = 15) and another recieved noninvasive ventilation (NIV group, n = 15). All patients were observed for the duration of ventilatory days, complications such as pneumonia and sepsis, length of the stay in ICU, and mortality. Statistical analysis was done using statistical software SPSS for windows (Version 16.0).
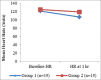
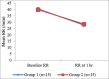
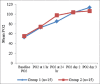
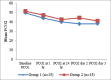
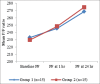
Results: There were no significant differences in age, sex, weight, and length of the stay in ICU in between the two groups. Rate of complications was significantly higher in ET group. Oxygenation was significantly improved in NIV group within 24 hr, later it become equivalent to the ET group patients while the pCO2 level was significantly lower in ET group compared with NIV group. Analgesia in both the groups is maintained to keep the visual analog scale (VAS) score below 2 and was comparable in both the groups.
Conclusions: The endotracheal intubation is also associated with serious complications as compared to NIV. The use of NIV in appropriate patients decreases complications, mortality, length of the stay in ICU, the use of resources, and cost.
Keywords: Chest trauma; ICU; flail chest; rib fracture; ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Flail chest injuries: a review of outcomes and treatment practices from the National Trauma Data Bank.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014 Feb;76(2):462-8. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000086. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014. PMID: 24458051
-
A comparative study of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and intermittent positive pressure ventilation (IPPV) in patients with flail chest.Emerg Med J. 2005 May;22(5):325-9. doi: 10.1136/emj.2004.019786. Emerg Med J. 2005. PMID: 15843697 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Risk factors for prolonged mechanical ventilation in patients with severe multiple injuries and blunt chest trauma: a single center retrospective case-control study.Acute Med Surg. 2018 Jan 31;5(2):166-172. doi: 10.1002/ams2.331. eCollection 2018 Apr. Acute Med Surg. 2018. PMID: 29657729 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from a large trauma center: impact of blunt chest trauma in polytrauma patients-still a relevant problem?Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2017 Apr 20;25(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13049-017-0384-y. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2017. PMID: 28427480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blunt thoracic trauma: recent advances and outstanding questions.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2015 Dec;21(6):544-8. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000251. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 26539928 Review.
Cited by
-
Noninvasive ventilation with a helmet in patients with acute respiratory failure caused by chest trauma: a randomized controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 8;10(1):21489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78607-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33293689 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An innovative technique of chest wall stabilization and reconstruction in traumatic flail chest: The figure-of-eight suture with polypropylene mesh and musculofascial flap.Chin J Traumatol. 2022 Mar;25(2):122-124. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2021.04.009. Epub 2021 May 6. Chin J Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34034947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardenheuer M, Obertacke U, Waydhas C, Nastkolb D. Epidemiology of severe multiple trauma—a prospective assessment of preclinical and clinical management. Unfallchirurg. 2000;103:355–63. - PubMed
-
- Clark CG, Schecter WP, Trunkey DD. Variables affecting outcome in blunt chest trauma: Flail chest vs pulmonary contusion. J Trauma. 1998;28:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Yeh DD, Kutcher ME, Knudson MM, Tang JF. Epidural analgesia for bluntthoracic injury—which patients benefit most? Injury. 2012;43:1667–71. - PubMed
-
- Wardhan R. Assessment and management of rib fracture pain in geriatric population: An ode to old age. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2013;26:626–31. - PubMed
-
- Liman ST, Kuzucu A, Tastepe AI, Ulasan GN, Topcu S. Chest injury due to blunt trauma. Eur J CardiothoracSurg. 2003;23:374–8. - PubMed

