Threonine Phosphorylation Fine-Tunes the Regulatory Activity of Histone-Like Nucleoid Structuring Protein in Salmonella Transcription
- PMID: 31333620
- PMCID: PMC6616471
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01515
Threonine Phosphorylation Fine-Tunes the Regulatory Activity of Histone-Like Nucleoid Structuring Protein in Salmonella Transcription
Abstract
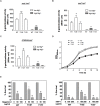
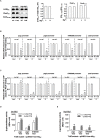
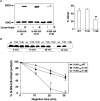
Histone-like nucleoid structuring protein (H-NS) in enterobacteria plays an important role in facilitating chromosome organization and functions as a crucial transcriptional regulator for global gene regulation. Here, we presented an observation that H-NS of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium could undergo protein phosphorylation at threonine 13 residue (T13). Analysis of the H-NS wild-type protein and its T13E phosphomimetic substitute suggested that T13 phosphorylation lead to alterations of H-NS structure, thus reducing its dimerization to weaken its DNA binding affinity. Proteomic analysis revealed that H-NS phosphorylation exerts regulatory effects on a wide range of genetic loci including the PhoP/PhoQ-regulated genes. In this study, we investigated an effect of T13 phosphorylation of H-NS that rendered transcription upregulation of the PhoP/PhoQ-activated genes. A lower promoter binding of the T13 phosphorylated H-NS protein was correlated with a stronger interaction of the PhoP protein, i.e., a transcription activator and also a competitor of H-NS, to the PhoP/PhoQ-dependent promoters. Unlike depletion of H-NS which dramatically activated the PhoP/PhoQ-dependent transcription even in a PhoP/PhoQ-repressing condition, mimicking of H-NS phosphorylation caused a moderate upregulation. Wild-type H-NS protein produced heterogeneously could rescue the phenotype of T13E mutant and fully restored the PhoP/PhoQ-dependent transcription enhanced by T13 phosphorylation of H-NS to wild-type levels. Therefore, our findings uncover a strategy in S. typhimurium to fine-tune the regulatory activity of H-NS through specific protein phosphorylation and highlight a regulatory mechanism for the PhoP/PhoQ-dependent transcription via this post-translational modification.
Keywords: bacterial signal transduction; histone-like nucleoid structuring protein (H-NS); post-translational modification; protein threonine phosphorylation; transcriptional regulation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An updated overview on the bacterial PhoP/PhoQ two-component signal transduction system.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jan 31;15:1509037. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1509037. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39958932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Dopamine-Responsive Signal Transduction Controls Transcription of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Virulence Genes.mBio. 2019 Apr 16;10(2):e02772-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02772-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30992361 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of the residue at position 48 in the Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium PhoQ sensor kinase.J Bacteriol. 2003 Mar;185(6):1935-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.6.1935-1941.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12618457 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontally acquired regulatory gene activates ancestral regulatory system to promote Salmonella virulence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Nov 4;48(19):10832-10847. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa813. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 33045730 Free PMC article.
-
The PhoQ/PhoP regulatory network of Salmonella enterica.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:7-21. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792679 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylation of xenogeneic silencer H-NS regulates biofilm development through the nitrogen homeostasis regulator in Shewanella.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 12;52(6):2886-2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1219. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38142446 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothesis: nucleoid-associated proteins segregate with a parental DNA strand to generate coherent phenotypic diversity.Theory Biosci. 2021 Feb;140(1):17-25. doi: 10.1007/s12064-020-00323-5. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Theory Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33095418
-
Pat- and Pta-mediated protein acetylation is required for horizontally-acquired virulence gene expression in Salmonella Typhimurium.J Microbiol. 2022 Aug;60(8):823-831. doi: 10.1007/s12275-022-2095-y. Epub 2022 May 27. J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35622226
-
Evolutionary and functional divergence of Sfx, a plasmid-encoded H-NS homolog, underlies the regulation of IncX plasmid conjugation.mBio. 2025 Feb 5;16(2):e0208924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02089-24. Epub 2024 Dec 23. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39714162 Free PMC article.
-
An updated overview on the bacterial PhoP/PhoQ two-component signal transduction system.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jan 31;15:1509037. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1509037. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39958932 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

