Liver-Derived TGF-β Maintains the EomeshiTbetlo Phenotype of Liver Resident Natural Killer Cells
- PMID: 31333651
- PMCID: PMC6616151
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01502
Liver-Derived TGF-β Maintains the EomeshiTbetlo Phenotype of Liver Resident Natural Killer Cells
Abstract
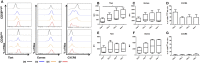
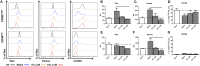
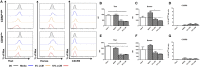
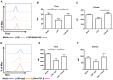
The adult human liver hosts a complex repertoire of liver resident and transient natural killer (NK) cell populations with diverse phenotypes and functions. Liver resident NK cells are CD56bright NK cells defined by a unique expression profile of transcription factors and cell surface markers (EomeshiTbetloTIGIT+CD69+CXCR6+CD49e-). Despite extensive characterization of the phenotype of liver resident NK cells, it remains unclear how factors within the liver microenvironment induce and maintain this unique phenotype. In this study, we have explored the factors regulating the phenotype of liver resident NK cells. Isolation of healthy liver resident NK cells from donor liver perfusate and in vitro culture results in the gradual loss of the characteristic Tbetlo phenotype, with the cells increasing Tbet expression significantly at day 7. This phenotypic loss could be halted through the dose-dependent addition of liver conditioned media (LCM), generated from the ex vivo culture of liver biopsies from healthy organ donors. TGF-β, but not IL-10, replicated the Tbet suppressive effects of LCM in both liver resident and peripheral blood NK cells. Furthermore, blocking TGF-β receptor signaling using the inhibitor SB431542, reversed the effect of LCM treatment on liver resident NK cells, causing the loss of tissue resident Eomeshi Tbetlo phenotype. Our findings identify liver-derived TGF-β as an important component of the liver microenvironment, which acts to regulate and maintain the phenotype of liver resident NK cells.
Keywords: Eomes; TBET; TGF-β1; liver-resident NK cell; microenviroment.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

