Unilateral Axilla-Bilateral Areola Approach for Thyroidectomy by da Vinci Robot: 500 Cases Treated by the Same Surgeon
- PMID: 31333802
- PMCID: PMC6636286
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.31463
Unilateral Axilla-Bilateral Areola Approach for Thyroidectomy by da Vinci Robot: 500 Cases Treated by the Same Surgeon
Abstract
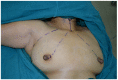
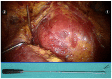
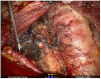
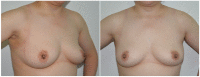
Objective: To investigate the efficacy and safety of da Vinci robot-assisted thyroidectomy via an unilateral axilla-bilateral areola (UABA) approach. Methods: The clinical data of 500 patients undergoing robotic thyroidectomy via an UABA approach from July 2014 to April 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. All 500 patients were operated on by the same surgeon and divided into two groups by the time sequence. The efficacy and complications were compared between the two groups. Results: Robotic thyroidectomy via an UABA approach was performed successfully in 500 cases, including 196 cases of benign thyroid diseases with a lesion diameter of 3.1 ± 1.3 cm (0.4 - 8.2 cm) and 304 cases of thyroid cancer with a tumor diameter of 1.2 ± 0.7 cm (0.4 - 4.4 cm). Surgical procedures included unilateral lobectomy and total thyroidectomy with or without central lymph node dissection. Among the 500 patients, 9 (1.8%) had transient recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, 1 (0.2%) had permanent unilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, 12 (2.4%) had subcutaneous hemorrhage of the trajectory area, and 6 (1.2%) had subcutaneous infection of the trajectory area after surgery. Among 239 thyroid cancer patients undergoing total thyroidectomy, 45 (18.8%) had transient hypoparathyroidism and 5 (2.1%) had permanent hypoparathyroidism. The incidence of permanent hypoparathyroidism was 1.9% (4/212) among the patients undergoing total thyroidectomy plus unilateral central lymph node dissection, and 3.7% (1/27) among the patients undergoing total thyroidectomy plus bilateral central lymph node dissection. During the follow-up of median 17 months, all patients were satisfied with postoperative appearance of the neck and no structural recurrence or metastases occurred. There was no significant difference in efficacy between the two groups (P > 0.05), while the complication rate in phase 2 was significantly lower than that in phase 1 (P < 0.05) as the surgeon became more proficient in the UABA approach. Conclusion: Robotic thyroidectomy via an UABA approach is simple, safe, and minimally invasive, suitable for radical resection of large benign tumors and early thyroid cancer and central lymph node dissection.
Keywords: da Vinci robot; efficacy; thyroidectomy; unilateral axilla-bilateral areola approach.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Arora A, Swords C, Garas G, Chaidas K, Prichard A, Budge J, Davies DC, Tolley N. The perception of scar cosmesis following thyroid and parathyroid surgery: A prospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2016;25:38–43. - PubMed
-
- Gagner M. Endoscopic subtotal parathyroidectomy in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Br J Surg. 1996;83(6):875. - PubMed
-
- Hüscher CS, Chiodini S, Napolitano C, Recher A. Endoscopic right thyroid lobectomy. Surg Endosc. 1997;11(8):877. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu K, Akira S, Jasmi AY, Kitamura Y, Kitagawa W, Akasu H, Tanaka S. Video-assisted neck surgery: endoscopic resection of thyroid tumors with a very minimal neck wound. J Am Coll Surg. 1999;188(6):697–703. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

