Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method development and validation for allyl isothiocyanate estimation in phytosomes of Brassica nigra extract
- PMID: 31334095
- PMCID: PMC6621346
- DOI: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_382_18
Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method development and validation for allyl isothiocyanate estimation in phytosomes of Brassica nigra extract
Abstract
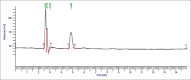
A simple, specific, accurate, precise, and robust reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method has been developed and validated for the estimation of allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) in phytosomes of black mustard extract (Brassica nigra). The method was validated with respect to specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness. The linearity was achieved over a range of 10-18 μg/mL and regression coefficient was obtained 0.9961. Accuracy of chromatographic method was evaluated by standard addition method; percentage recovery attained was 97.07 ± 0.008-103.66 ± 0.013. Relative standard deviation for intraday and interday precision was 0.02% and 0.22%, respectively. The limit of detection and limit of quantification of the AITC were found to be 0.0043 μg/mL and 0.01324 μg/mL, respectively. This result shows that the method was well validated. In the present study, the AITC content was found 0.0009% ± 0.014% in black mustard. This study reveals that the proposed high-performance thin-layer chromatography method is accurate, fast, and cost-effective for the routine estimation of AITC in the phytosome formulation.
Keywords: Allyl isothiocyanate; Brassica nigra; phytosome analysis; reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method development.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Khan J, Alexander A, Saraf S, Saraf S. Recent advances and future prospects of phyto-phospholipid complexation technique for improving pharmacokinetic profile of plant actives. Journal of controlled release. 2013;168:50–60. - PubMed
-
- Asfaw Z. Traditional African Vegetables: Proceedings of the IPGRI International Workshop on Genetic Resources of TraditionalVegetables in Africa. Conservation and Use. ICRAF-HQ, Nairobi. Rome: Institute of Plant Genetic and Crop Plant Research; 1997. Conservation and use of traditional vegetables in Ethiopia; pp. 57–65.
-
- Lim TK. Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants. Netherlands: Springer; 2014. Muscari neglectum; pp. 122–5.
-
- Morris TN. Microscopic analysis of cattle-foods. Chicago: Cambridge University Press; 2015.
-
- Krishnaveni M, Saranya S. Gas chromatography-mass spectrophotometry analysis of phytochemicals in Brassica hirta seeds. Int J Adv Life Sci. 2016;9:243–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
