Density of Macrophages Immunostained With Anti-iba1 Antibody in the Vestibular Endorgans After Cochlear Implantation in the Human
- PMID: 31335797
- PMCID: PMC6697207
- DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002313
Density of Macrophages Immunostained With Anti-iba1 Antibody in the Vestibular Endorgans After Cochlear Implantation in the Human
Abstract
Hypothesis: Cochlear implantation may result in an increase in the density of macrophages in vestibular endorgans in the human.
Background: Vestibular symptoms are a common complication of cochlear implantation. In a previous study, we demonstrated histological evidence of a foreign-body response caused by silicon and platinum in the human cochlea following cochlear implantation. The objective of the current study was to seek evidence of a possible immune response in vestibular endorgans after cochlear implantation.
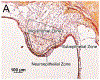
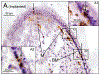
Methods: The density of macrophages immunostained with anti-Iba1 antibody in the vestibular endorgans (lateral and posterior semicircular canals, utricle and saccule) in 10 human subjects who had undergone unilateral cochlear implantation was studied by light microscopy. The densities of macrophages in the neuroepithelium, subepithelial stroma, and among dendritic processes in the mid-stromal zone in four vestibular endorgans in the implanted and the opposite unimplanted ears were compared. The distributions of macrophage morphology (amoeboid, transitional and ramified) were also compared.
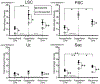
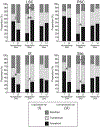
Results: The densities of macrophages in implanted ears in four vestibular endorgans were significantly greater than that in opposite unimplanted ears except in the subepithelial zone of the utricle and posterior semicircular canal. In contrast to the neuroepithelium, the subepithelial distribution of amoeboid macrophages in implanted ears was significantly less than in unimplanted ears.
Conclusion: An increase in the density of macrophages in four vestibular endorgans after implantation was demonstrated. The transition among phenotype of macrophages suggested possible migration of amoeboid macrophages from the subepithelial stroma into the neuroepithelium.
Conflict of interest statement
(disclosure)
All authors declare no conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Figures









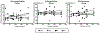
References
-
- Fina M, Skinner M, Goebel JA, Piccirillo JF, Neely JG. Vestibular dysfunction after cochlear implantation. Otol Neurotol. 2003, 24: 234–242. - PubMed
-
- Terry B, Kelt RE, Jeyakumar A. Delayed complications after cochlear implantation. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141: 1012–1017. - PubMed
-
- Ito J Influence of the multichannel cochlear implant on vestibular function. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998, 118: 900–902. - PubMed
-
- Kubo T, Yamamoto KI, Iwaki T, Doi K, Tamura M. Different forms of dizziness occurring after cochlear implant. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2001, 258: 9–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

