Challenges and perspectives for structural biology of lncRNAs-the example of the Xist lncRNA A-repeats
- PMID: 31336384
- PMCID: PMC6917512
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz086
Challenges and perspectives for structural biology of lncRNAs-the example of the Xist lncRNA A-repeats
Abstract
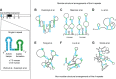
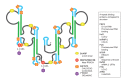
Following the discovery of numerous long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) transcripts in the human genome, their important roles in biology and human disease are emerging. Recent progress in experimental methods has enabled the identification of structural features of lncRNAs. However, determining high-resolution structures is challenging as lncRNAs are expected to be dynamic and adopt multiple conformations, which may be modulated by interaction with protein binding partners. The X-inactive specific transcript (Xist) is necessary for X inactivation during dosage compensation in female placental mammals and one of the best-studied lncRNAs. Recent progress has provided new insights into the domain organization, molecular features, and RNA binding proteins that interact with distinct regions of Xist. The A-repeats located at the 5' end of the transcript are of particular interest as they are essential for mediating silencing of the inactive X chromosome. Here, we discuss recent progress with elucidating structural features of the Xist lncRNA, focusing on the A-repeats. We discuss the experimental and computational approaches employed that have led to distinct structural models, likely reflecting the intrinsic dynamics of this RNA. The presence of multiple dynamic conformations may also play an important role in the formation of the associated RNPs, thus influencing the molecular mechanism underlying the biological function of the Xist A-repeats. We propose that integrative approaches that combine biochemical experiments and high-resolution structural biology in vitro with chemical probing and functional studies in vivo are required to unravel the molecular mechanisms of lncRNAs.
Keywords: Xist; chemical probing; computational structure prediction; enzymatic footprinting; lncRNA; structural biology.
© The Author(s) (2019). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, IBCB, SIBS, CAS.
Figures


References
-
- Brockdorff N. (1992). The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell 71, 515–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

