Deep sternal wound infections: Evidence for prevention, treatment, and reconstructive surgery
- PMID: 31336416
- PMCID: PMC6657195
- DOI: 10.5999/aps.2018.01151
Deep sternal wound infections: Evidence for prevention, treatment, and reconstructive surgery
Abstract
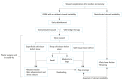
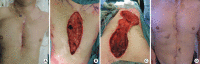
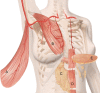
Median sternotomy is the most popular approach in cardiac surgery. Post-sternotomy wound complications are rare, but the occurrence of a deep sternal wound infection (DSWI) is a catastrophic event associated with higher morbidity and mortality, longer hospital stays, and increased costs. A literature review was performed by searching PubMed from January 1996 to August 2017 according to the guidelines in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement. The following keywords were used in various combinations: DSWI, post-sternotomy complication, and sternal reconstruction. Thirty-nine papers were included in our qualitative analysis, in which each aspect of the DSWI-related care process was analyzed and compared to the actual standard of care. Plastic surgeons are often involved too late in such clinical scenarios, when previous empirical treatments have failed and a definitive reconstruction is needed. The aim of this comprehensive review was to create an up-to-date operative flowchart to prevent and properly treat sternal wound infection complications after median sternotomy.
Keywords: Infection; Reconstructive surgical procedure; Sternotomy; Sternum.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- McGregor WE, Trumble DR, Magovern JA. Mechanical analysis of midline sternotomy wound closure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999;117:1144–50. - PubMed
-
- Cayci C, Russo M, Cheema FH, et al. Risk analysis of deep sternal wound infections and their impact on long-term survival: a propensity analysis. Ann Plast Surg. 2008;61:294–301. - PubMed
-
- Sjogren J, Malmsjo M, Gustafsson R, et al. Poststernotomy mediastinitis: a review of conventional surgical treatments, vacuum-assisted closure therapy and presentation of the Lund University Hospital mediastinitis algorithm. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;30:898–905. - PubMed
-
- Tang AT, Ohri SK, Haw MP. Novel application of vacuum assisted closure technique to the treatment of sternotomy wound infection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2000;17:482–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

