Acute Supplementation with Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice Causes a Greater Increase in Plasma Nitrite and Reduction in Blood Pressure of Older Compared to Younger Adults
- PMID: 31336633
- PMCID: PMC6683255
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11071683
Acute Supplementation with Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice Causes a Greater Increase in Plasma Nitrite and Reduction in Blood Pressure of Older Compared to Younger Adults
Abstract
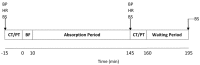
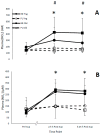
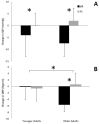
Nitrate-rich beetroot juice supplementation has been shown to improve cardiovascular and cognitive function in younger and older adults via increased nitric oxide production. However, it is unclear whether the level of effects differs between the two groups. We hypothesized that acute supplementation with nitrate-rich beetroot juice would improve cardiovascular and cognitive function in older and younger adults, with the potential for greater improvements in older adults. Thirteen younger (18-30 years) and 11 older (50-70 years) adults consumed either 150 mL of nitrate-rich beetroot juice (BR; 10.5 mmol nitrate) or placebo (PL; 1 mmol nitrate) in a double-blind, crossover design, 2.25 h prior to a 30-min treadmill walk. Plasma nitrate and nitrite concentrations, blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), cognitive function, mood and perceptual tests were performed throughout the trial. BR consumption significantly increased plasma nitrate (p < 0.001) and nitrite (p = 0.003) concentrations and reduced systolic BP (p < 0.001) in both age groups and reduced diastolic BP (p = 0.013) in older adults. Older adults showed a greater elevation in plasma nitrite (p = 0.038) and a greater reduction in diastolic BP (p = 0.005) following BR consumption than younger adults. Reaction time was improved in the Stroop test following BR supplementation for both groups (p = 0.045). Acute BR supplementation increased plasma nitrite concentrations and reduced diastolic BP to a greater degree in older adults; whilst systolic BP was reduced in both older and younger adults, suggesting nitrate-rich BR may improve cardiovascular health, particularly in older adults due to the greater benefits from reductions in diastolic BP.
Keywords: aging; beetroot juice; blood pressure; cognition; nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division . World Population Ageing. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2015.
-
- Velmurugan S., Gan J.M., Rathod K.S., Khambata R.S., Ghosh S.M., Hartley A., Van Eijl S., Sagi-Kiss V., Chowdhury T.A., Curtis M., et al. Dietary nitrate improves vascular function in patients with hypercholesterolemia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016;103:25–38. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.116244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kelly J., Fulford J., Vanhatalo A., Blackwell J.R., French O., Bailey S.J., Gilchrist M., Winyard P.G., Jones A.M. Effects of short-term dietary nitrate supplementation on blood pressure, O2 uptake kinetics, and muscle and cognitive function in older adults. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013;304:R73–R83. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00406.2012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bailey S.J., Vanhatalo A., Winyard P.G., Jones A.M. The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway: Its role in human exercise physiology. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2012;12:309–320. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2011.635705. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

