Proteomic Analysis of Breast Cancer Resistance to the Anticancer Drug RH1 Reveals the Importance of Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 31336714
- PMCID: PMC6678540
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11070972
Proteomic Analysis of Breast Cancer Resistance to the Anticancer Drug RH1 Reveals the Importance of Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
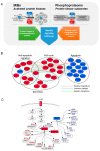
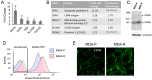
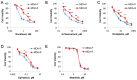
Antitumor drug resistance remains a major challenge in cancer chemotherapy. Here we investigated the mechanism of acquired resistance to a novel anticancer agent RH1 designed to be activated in cancer cells by the NQO1 enzyme. Data show that in some cancer cells RH1 may act in an NQO1-independent way. Differential proteomic analysis of breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to RH1 revealed changes in cell energy, amino acid metabolism and G2/M cell cycle transition regulation. Analysis of phosphoproteomics and protein kinase activity by multiplexed kinase inhibitor beads showed an increase in the activity of protein kinases involved in the cell cycle and stemness regulation and downregulation of proapoptotic kinases such as JNK in RH1-resistant cells. Suppression of JNK leads to the increase of cancer cell resistance to RH1. Moreover, resistant cells have enhanced expression of stem cell factor (SCF) and stem cell markers. Inhibition of SCF receptor c-KIT resulted in the attenuation of cancer stem cell enrichment and decreased amounts of tumor-initiating cells. RH1-resistant cells also acquire resistance to conventional therapeutics while remaining susceptible to c-KIT-targeted therapy. Data show that RH1 can be useful to treat cancers in the NQO1-independent way, and targeting of the cancer stem cells might be an effective approach for combating resistance to RH1 therapy.
Keywords: JNK; MIBs; RH1; c-KIT; cancer drug resistance; cancer stem cells; chemotherapy; label-free proteomics; phosphoproteome; protein kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abubaker K., Latifi A., Luwor R., Nazaretian S., Zhu H., Quinn M.A., Thompson E.W., Findlay J.K., Ahmed N. Short-term single treatment of chemotherapy results in the enrichment of ovarian cancer stem cell-like cells leading to an increased tumor burden. Mol. Cancer. 2013;12:24. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-24. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

