Access to Kidney Transplantation after a Failed First Kidney Transplant and Associations with Patient and Allograft Survival: An Analysis of National Data to Inform Allocation Policy
- PMID: 31337621
- PMCID: PMC6682813
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01530219
Access to Kidney Transplantation after a Failed First Kidney Transplant and Associations with Patient and Allograft Survival: An Analysis of National Data to Inform Allocation Policy
Abstract
Background and objectives: Patients who have failed a transplant are at increased risk of repeat transplant failure. We determined access to transplantation and transplant outcomes in patients with and without a history of transplant failure.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: In this observational study of national data, the proportion of waitlisted patients and deceased donor transplant recipients with transplant failure was determined before and after the new kidney allocation system. Among patients initiating maintenance dialysis between May 1995 and December 2014, the likelihood of deceased donor transplantation was determined in patients with (n=27,459) and without (n=1,426,677) a history of transplant failure. Among transplant recipients, allograft survival, the duration of additional kidney replacement therapy required within 10 years of transplantation, and the association of transplantation versus dialysis with mortality was determined in patients with and without a history of transplant failure.
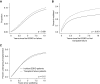
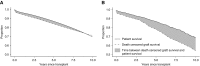
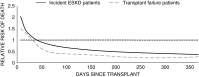
Results: The proportion of waitlist candidates (mean 14%) and transplant recipients (mean 12%) with transplant failure did not increase after the new kidney allocation system. Among patients initiating maintenance dialysis, transplant-failure patients had a higher likelihood of transplantation (hazard ratio [HR], 1.16; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 1.12 to 1.20; P<0.001). Among transplant recipients, transplant-failure patients had a higher likelihood of death-censored transplant failure (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.34 to 1.54; P<0.001) and a greater need for additional kidney replacement therapy required within 10 years after transplantation (mean, 9.0; 95% CI, 5.4 to 12.6 versus mean, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.5 to 2.7 months). The association of transplantation versus dialysis with mortality was clinically similar in waitlisted patients with (HR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.29 to 0.35; P<0.001) and without transplant failure (HR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.39 to 0.41; P<0.001).
Conclusions: Transplant-failure patients initiating maintenance dialysis have a higher likelihood of transplantation than transplant-naïve patients. Despite inferior death-censored transplant survival, transplantation was associated with a similar reduction in the risk of death compared with treatment with dialysis in patients with and without a prior history of transplant failure.
Keywords: Allografts; Graft Survival; Homologous; Renal Replacement Therapy; Transplant Recipients; Transplantation; United States Renal Data System; Waiting Lists; dialysis; kidney transplantation; mortality risk; transplant outcomes.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Patient-Centered Outcomes with Second Kidney Transplant.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Aug 7;14(8):1131-1132. doi: 10.2215/CJN.07400619. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31337622 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kaplan B, Meier-Kriesche HU: Death after graft loss: An important late study endpoint in kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 2: 970–974, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Knoll G, Muirhead N, Trpeski L, Zhu N, Badovinac K: Patient survival following renal transplant failure in Canada. Am J Transplant 5: 1719–1724, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Johnston O, Zalunardo N, Rose C, Gill JS: Prevention of sepsis during the transition to dialysis may improve the survival of transplant failure patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 1331–1337, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Johnston O, Rose C, Landsberg D, Gourlay WA, Gill JS: Nephrectomy after transplant failure: Current practice and outcomes. Am J Transplant 7: 1961–1967, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

