Perturbation of the interactions of calmodulin with GRK5 using a natural product chemical probe
- PMID: 31337679
- PMCID: PMC6689901
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1818547116
Perturbation of the interactions of calmodulin with GRK5 using a natural product chemical probe
Abstract
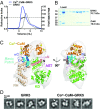
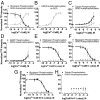
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinases (GRKs) are responsible for initiating desensitization of activated GPCRs. GRK5 is potently inhibited by the calcium-sensing protein calmodulin (CaM), which leads to nuclear translocation of GRK5 and promotion of cardiac hypertrophy. Herein, we report the architecture of the Ca2+·CaM-GRK5 complex determined by small-angle X-ray scattering and negative-stain electron microscopy. Ca2+·CaM binds primarily to the small lobe of the kinase domain of GRK5 near elements critical for receptor interaction and membrane association, thereby inhibiting receptor phosphorylation while activating the kinase for phosphorylation of soluble substrates. To define the role of each lobe of Ca2+·CaM, we utilized the natural product malbrancheamide as a chemical probe to show that the C-terminal lobe of Ca2+·CaM regulates membrane binding while the N-terminal lobe regulates receptor phosphorylation and kinase domain activation. In cells, malbrancheamide attenuated GRK5 nuclear translocation and effectively blocked the hypertrophic response, demonstrating the utility of this natural product and its derivatives in probing Ca2+·CaM-dependent hypertrophy.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5; calmodulin; hypertrophy; malbrancheamide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chuang T. T., Paolucci L., De Blasi A., Inhibition of G protein-coupled receptor kinase subtypes by Ca2+/calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 28691–28696 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Pronin A. N., Satpaev D. K., Slepak V. Z., Benovic J. L., Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases by calmodulin and localization of the calmodulin binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18273–18280 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Levay K., Satpaev D. K., Pronin A. N., Benovic J. L., Slepak V. Z., Localization of the sites for Ca2+-binding proteins on G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Biochemistry 37, 13650–13659 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

