Amorphous solid dispersion of Berberine mitigates apoptosis via iPLA2β/Cardiolipin/Opa1 pathway in db/db mice and in Palmitate-treated MIN6 β-cells
- PMID: 31337982
- PMCID: PMC6643135
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.32020
Amorphous solid dispersion of Berberine mitigates apoptosis via iPLA2β/Cardiolipin/Opa1 pathway in db/db mice and in Palmitate-treated MIN6 β-cells
Abstract
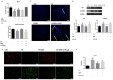
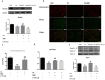
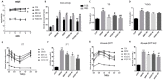
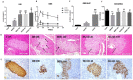
Aims: Berberine (BBR) improves beta-cell function in Type 2 diabetes (T2D) because of its anti-apoptotic activity, and our laboratory developed a new preparation named Huang-Gui Solid Dispersion (HGSD) to improve the oral bioavailability of BBR. However, the mechanism by which BBR inhibits beta-cell apoptosis is unclear. We hypothesized that the Group VIA Ca2+-Independent Phospholipase A2 (iPLA2β)/Cardiolipin(CL)/Opa1 signaling pathway could exert a protective role in T2D by regulating beta-cell apoptosis and that HGSD could inhibit β-cell apoptosis through iPLA2β/CL/Opa1 upregulation. Methods: We examined how iPLA2β and BBR regulated apoptosis and insulin secretion through CL/Opa1 in vivo and in vitro. In in vitro studies, we developed Palmitate(PA)-induced apoptotic cell death model in mouse insulinoma cells (MIN6). iPLA2β overexpression and silencing technology were used to examine how the iPLA2β/CL/Opa1 interaction may play an important role in BBR treatment. In in vivo studies, db/db mice were used as a diabetic animal model. The pancreatic islet function and morphology, beta-cell apoptosis and mitochondrial injury were examined to explore the effects of HGSD. The expression of iPLA2β/CL/Opa1 was measured to explore whether the signaling pathway was damaged in T2D and was involved in HGSD treatment. Results: The overexpression of iPLA2β and BBR treatment significantly attenuated Palmitate- induced mitochondrial injury and apoptotic death compared with Palmitate-treated MIN6 cell. In addition, iPLA2β silencing could simultaneously partly abolish the anti-apoptotic effect of BBR and decrease CL/Opa1 signaling in MIN6 cells. Moreover, HGSD treatment significantly decreased beta-cell apoptosis and resulted in the upregulation of iPLA2β/CL/Opa1 compared to those of the db/db mice. Conclusion: The results indicated that the regulation of iPLA2β/CL/Opa1 by HGSD may prevent beta-cell apoptosis and may improve islet beta-cell function in Type 2 diabetic mice and in palmitate-treated MIN6 cells.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Berberine.; Beta-cell dysfunction; Cardiolipin; Dynamin-related protein(Opa1); Group VIA Ca2+-Independent Phospholipase A2 (iPLA2β); Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Smyth S, Heron A. Diabetes and obesity: the twin epidemics. Nat Med. 2006;12(1):75–80. - PubMed
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52(1):102–10. - PubMed
-
- Rhodes CJ. Type 2 diabetes-a matter of beta-cell life and death? Science. 2005;307(5708):380–4. - PubMed
-
- Lei X, Zhang S, Barbour SE, Bohrer A, Ford EL, Koizumi A. et al. Spontaneous development of endoplasmic reticulum stress that can lead to diabetes mellitus is associated with higher calcium-independent phospholipase A2 expression: a role for regulation by SREBP-1. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(9):6693–705. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

