Liver Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats: Protective Role of Artemisia Turanica
- PMID: 31338251
- PMCID: PMC6645339
- DOI: 10.3831/KPI.2019.22.014
Liver Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats: Protective Role of Artemisia Turanica
Abstract
Objectives: Oxidative stress plays a central role in diabetes-induced complications. In the present study, the protevtive effect of Artemisia turanica (A. turanica) was evaluated against diabetes-induced liver oxidative stress and dysfunction.
Methods: Fifty male Wistar rats were randomly divided into five groups: control, diabetic, diabetic + metformin, diabetic + A. turanica extract, and diabetic + A. turanica extract + metformin. Experimental diabetes was induced by a single-dose (55 mg/kg, intraperitoneally (ip)) injection of streptozotocin (STZ). Metformin (300 mg/kg) and A. turanica extract (70 mg/kg) were orally administrated three days after STZ injection for four weeks. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), total thiol content and superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase activities were measured in the liver tissue. Serum glucose concentration, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities were also determined.
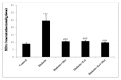
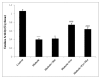
Results: In the diabetic group, serum glucose concentration, serum AST and ALT activities and liver MDA level were significantly higher while tissue total thiol content as well as catalase and SOD activities were lower, compared to the control group. Serum glucose in diabetic rats treated with metformin + A. turanica extract showed a significant decrease compared with the diabetic group. In all the A. turanica extract and metformin treated groups, serum ALT, tissue MDA level, total thiol content and SOD activity significantly improved compared with the diabetic rats. However, treatment of the diabetic rats only with metformin could not significantly change the activities of catalase and AST compared with the diabetic group.
Conclusion: These findings suggested that A. turanica extract had a therapeutic effect on liver dysfuncyion and oxidative stress induced by diabetes, that may be probably due to its antioxidant and antiinflammatory effects.
Keywords: artemisia turanica; diabetes mellitus; metformin; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of Artemisia turanica extract on renal oxidative and biochemical markers in STZ-induced diabetes in rat.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2020 Sep-Oct;10(5):504-512. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2020. PMID: 32995328 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Cinnamomum cassia extract on oxidative stress in the liver and kidney of STZ-induced diabetic rats.J Complement Integr Med. 2021 Sep 10;19(2):311-321. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2021-0142. eCollection 2022 Jun 1. J Complement Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 34506695
-
Protective effects of Artemisia judaica extract compared to metformin against hepatorenal injury in high-fat diet/streptozotocine-induced diabetic rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Nov;27(32):40525-40536. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09997-2. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32666453
-
THE EFFECT OF MELATONIN AGAINST GASTRIC OXIDATIVE STRESS AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN STREPTOZOTOCIN-INDUCED DIABETIC RATS.Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2018 Oct-Dec;14(4):453-458. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2018.453. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2018. PMID: 31149296 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of anthocyanin-rich blackberry juice on endoplasmic reticulum stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Jul;30(32):79067-79081. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-27827-z. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37280499 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the Chemical Composition, Antihyperglycemic and Antilipidemic Effects of Bassia eriophora and Its Derived Constituent, Umbelliferone on High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Molecules. 2022 Oct 16;27(20):6941. doi: 10.3390/molecules27206941. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296534 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of Dodonaea viscosa extract against streptozotocin-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Aug;31(8):101669. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37576853 Free PMC article.
-
Lippia javanica (Burm. F.) Herbal Tea: Modulation of Hepatoprotective Effects in Chang Liver Cells via Mitigation of Redox Imbalance and Modulation of Perturbed Metabolic Activities.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 7;14:1221769. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1221769. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37608895 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of S-adenosyl methionine on oxidative stress and tissue damage in STZ-induced diabetic rats.Amino Acids. 2025 Jul 31;57(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00726-025-03471-4. Amino Acids. 2025. PMID: 40742482 Free PMC article.
-
Dapagliflozin, Liraglutide, and Their Combination Attenuate Diabetes Mellitus-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury-Insight into Oxidative Injury/Inflammation/Apoptosis Modulation.Life (Basel). 2022 May 21;12(5):764. doi: 10.3390/life12050764. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ruch W, Zumsteg U. Diabetes or hyperglycemia? Schweizerische medizinische Wochenschrift. 1988;118(8):264–266. - PubMed
-
- Levinthal GN, Tavill AS. Liver disease and diabetes mellitus. Clinical diabetes. 1999;17(2):73.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
