Small Nucleolar RNAs: Insight Into Their Function in Cancer
- PMID: 31338327
- PMCID: PMC6629867
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00587
Small Nucleolar RNAs: Insight Into Their Function in Cancer
Abstract
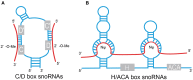
Small nucleolar RNAs (SnoRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs divided into two classes: C/D box snoRNAs and H/ACA box snoRNAs. The canonical function of C/D box and H/ACA box snoRNAs are 2'-O-ribose methylation and pseudouridylation of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), respectively. Emerging evidence has demonstrated that snoRNAs are involved in various physiological and pathological cellular processes. Mutations and aberrant expression of snoRNAs have been reported in cell transformation, tumorigenesis, and metastasis, indicating that snoRNAs may serve as biomarkers and/or therapeutic targets of cancer. Hence, further study of the functions and underlying mechanism of snoRNAs is valuable. In this review, we summarize the biogenesis and functions of snoRNAs, as well as the association of snoRNAs in different types of cancers and their potential roles in cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; mRNA splicing; rRNA processing; sdRNA; small nucleolar RNA; therapy.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

