The long non-coding RNA H19: an active player with multiple facets to sustain the hallmarks of cancer
- PMID: 31338555
- PMCID: PMC11105575
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03240-z
The long non-coding RNA H19: an active player with multiple facets to sustain the hallmarks of cancer
Abstract
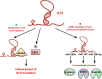
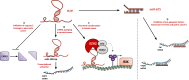
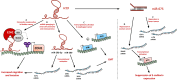
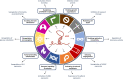
Cancer cells exhibit hallmarks in terms of proliferation, resistance to cell death, angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, and genomic instability. Despite the progress in cancer research and the comprehension of tumorigenesis mechanisms, cancer remains a major issue in public health. A better understanding of the molecular factors associated with the appearance or progression of cancer may allow the development of therapeutic alternatives. Increasing data highlight the role of long non-coding RNAs in many diseases, including cancer. The long non-coding RNA H19 was the first discovered riboregulator, and it has been shown to be involved at multiple steps of tumorigenesis. Indeed, this lncRNA exert its action at various molecular scales. Understanding the role of H19 in cancer progression may allow to set up therapeutic strategies to prevent tumor expansion and metastatic dissemination. In this review, we will summarize the overexpression of the long non-coding RNA H19 in several types of cancer and the multiple implications of the long non-coding RNA H19 in the different hallmarks that define human cancer.
Keywords: H19; Hallmarks of cancer; Metastasis; Proliferation; lncRNA; miRNA.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

