Transcriptional initiation of a small RNA, not R-loop stability, dictates the frequency of pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- PMID: 31338863
- PMCID: PMC6800796
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14356
Transcriptional initiation of a small RNA, not R-loop stability, dictates the frequency of pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
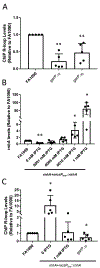
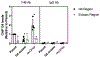
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the sole causative agent of gonorrhea, constitutively undergoes diversification of the Type IV pilus. Gene conversion occurs between one of the several donor silent copies located in distinct loci and the recipient pilE gene, encoding the major pilin subunit of the pilus. A guanine quadruplex (G4) DNA structure and a cis-acting sRNA (G4-sRNA) are located upstream of the pilE gene and both are required for pilin antigenic variation (Av). We show that the reduced sRNA transcription lowers pilin Av frequencies. Extended transcriptional elongation is not required for Av, since limiting the transcript to 32 nt allows for normal Av frequencies. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays, we show that cellular G4s are less abundant when sRNA transcription is lower. In addition, using ChIP, we demonstrate that the G4-sRNA forms a stable RNA:DNA hybrid (R-loop) with its template strand. However, modulating R-loop levels by controlling RNase HI expression does not alter G4 abundance quantified through ChIP. Since pilin Av frequencies were not altered when modulating R-loop levels by controlling RNase HI expression, we conclude that transcription of the sRNA is necessary, but stable R-loops are not required to promote pilin Av.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

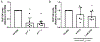

Similar articles
-
Altering the Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilE Guanine Quadruplex Loop Bases Affects Pilin Antigenic Variation.Biochemistry. 2020 Mar 17;59(10):1104-1112. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b01038. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32078293 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription of a cis-acting, noncoding, small RNA is required for pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Jan;9(1):e1003074. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003074. Epub 2013 Jan 17. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23349628 Free PMC article.
-
A Double-Strand Break Does Not Promote Neisseria gonorrhoeae Pilin Antigenic Variation.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jun 10;201(13):e00256-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00256-19. Print 2019 Jul 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30988037 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative model for Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilin variation.Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):107-9. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80009-4. Vaccine. 1988. PMID: 2898841 Review.
-
Pilin gene variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: reassessing the old paradigms.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009 May;33(3):521-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00171.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19396954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and implementation of a Type I-C CRISPR-based programmable repression system for Neisseria gonorrhoeae.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0302523. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03025-23. Epub 2023 Dec 21. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38126782 Free PMC article.
-
RAD51-mediated R-loop formation acts to repair transcription-associated DNA breaks driving antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Nov 28;120(48):e2309306120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2309306120. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37988471 Free PMC article.
-
PacBio Amplicon Sequencing Method To Measure Pilin Antigenic Variation Frequencies of Neisseria gonorrhoeae.mSphere. 2019 Oct 2;4(5):e00562-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00562-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31578246 Free PMC article.
-
Microevolution and Its Impact on Hypervirulence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Vaccine Escape in Neisseria meningitidis.Microorganisms. 2023 Dec 18;11(12):3005. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11123005. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38138149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flipons and small RNAs accentuate the asymmetries of pervasive transcription by the reset and sequence-specific microcoding of promoter conformation.J Biol Chem. 2023 Sep;299(9):105140. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105140. Epub 2023 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37544644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexeyev MF (1995) Three kanamycin resistance gene cassettes with different polylinkers. BioTechniques 18: 52, 54,, 56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

