Activated M2 Macrophages Contribute to the Pathogenesis of IgG4-Related Disease via Toll-like Receptor 7/Interleukin-33 Signaling
- PMID: 31339007
- PMCID: PMC6972995
- DOI: 10.1002/art.41052
Activated M2 Macrophages Contribute to the Pathogenesis of IgG4-Related Disease via Toll-like Receptor 7/Interleukin-33 Signaling
Abstract
Objective: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a unique inflammatory disorder in which Th2 cytokines promote IgG4 production. In addition, recent studies have implicated the Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathway. This study was undertaken to examine the expression of TLRs in salivary glands (SGs) from patients with IgG4-RD.
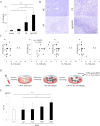
Methods: SGs from 15 patients with IgG4-RD, 15 patients with Sjögren's syndrome (SS), 10 patients with chronic sialadenitis, and 10 healthy controls were examined histologically. TLR family gene expression (TLR-1 through TLR-10) was analyzed by DNA microarray in the submandibular glands (SMGs). Up-regulation of TLRs was confirmed in SGs from patients with IgG4-RD. Finally, the phenotype of human TLR-7 (huTLR-7)-transgenic C57BL/6 mice was assessed before and after stimulation with TLR agonist.
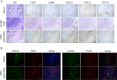
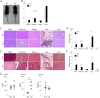
Results: In patients with IgG4-RD, TLR-4, TLR-7, TLR-8, and TLR-9 were overexpressed. Polymerase chain reaction validated the up-regulation of TLR-7 in IgG4-RD compared with the other groups. Immunohistochemical analysis confirmed strong infiltration of TLR-7-positive cells in the SGs of patients with IgG4-RD. Double immunohistochemical staining showed that TLR-7 expression colocalized with CD163+ M2 macrophages. After in vitro stimulation with a TLR-7 agonist, CD163+ M2 macrophages produced higher levels of interleukin-33 (IL-33), which is a Th2-activating cytokine. In huTLR-7-transgenic mice, the focus and fibrosis scores in SMGs, pancreas, and lungs were significantly higher than those in wild-type mice (P < 0.05). Moreover, the concentration of serum IgG, IgG1, and IL-33 in huTLR-7-transgenic mice was distinctly increased upon stimulation with a TLR-7 agonist (P < 0.05).
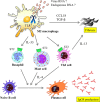
Conclusion: TLR-7-expressing M2 macrophages may promote the activation of Th2 immune responses via IL-33 secretion in IgG4-RD.
© 2019 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures


References
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2001;344:732–8. - PubMed
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4‐related disease. N Engl J Med 2012;366:539–51. - PubMed
-
- Nirula A, Glaser SM, Kalled SL, Taylor FR. What is IgG4? A review of the biology of a unique immunoglobulin subtype. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011;23:119–24. - PubMed
-
- Finkelman FD, Boyce JA, Vercelli D, Rothenberg ME. Key advances in mechanisms of asthma, allergy, and immunology in 2009. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125:312–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

