Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status
- PMID: 31339012
- PMCID: PMC6712228
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0067
Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to investigate the prevalence, management, and comorbidities of diabetes among Korean adults aged 30 years and older.
Methods: This study used 2013 to 2016 data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a nationally-representative survey of the Korean population. Diabetes was defined as fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dL, current use of antidiabetic medication, a previous history of diabetes, or glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%.
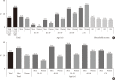
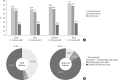
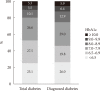
Results: In 2016, 14.4% (approximately 5.02 million) of Korean adults had diabetes. The prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 25.3% (8.71 million). From 2013 to 2016, the awareness, control, and treatment rates for diabetes were 62.6%, 56.7%, and 25.1%, respectively. People with diabetes had the following comorbidities: obesity (50.4%), abdominal obesity (47.8%), hypertension (55.3%), and hypercholesterolemia (34.9%). The 25.1%, 68.4%, and 44.2% of people with diabetes achieved HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure <140/85 mm Hg, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL. Only 8.4% of people with diabetes had good control of all three targets.
Conclusion: This study confirms that diabetes is as an important public health problem. Efforts should be made to increase awareness, detection, and comprehensive management of diabetes to reduce diabetes-related morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Comorbidity; Diabetes mellitus; Hypercholesterolemia; Hypertension; Nutrition surveys; Obesity; Prevalence; Public health; Republic of Korea.
Copyright © 2019 Korean Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

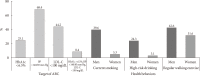
References
-
- Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett PH, Mathers C, Tuomilehto J, Nag S, Connolly V, King H. The burden of mortality attributable to diabetes: realistic estimates for the year 2000. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2130–2135. - PubMed
-
- Morrish NJ, Wang SL, Stevens LK, Fuller JH, Keen H. Mortality and causes of death in the WHO multinational study of vascular disease in diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001;44(Suppl 2):S14–S21. - PubMed
-
- Jeon JY, Kim DJ, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Lim S, Choi SH, Kim CS, An JH, Kim NH, Won JC, Kim JH, Cha BY, Song KH Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Current status of glycemic control of patients with diabetes in Korea: the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38:197–203. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vital Statistics Division Statistics Korea. Shin HY, Lee JY, Kim JE, Lee S, Youn H, Kim H, Lee J, Park MS, Huh S. Cause-of-death statistics in 2016 in the Republic of Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2018;61:573–584.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

