Recovery of Gram-Negative Bacteria from Aerobic Blood Culture Bottles Containing Antibiotic Binding Resins after Exposure to β-Lactam and Fluoroquinolone Concentrations
- PMID: 31340990
- PMCID: PMC6760962
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00849-19
Recovery of Gram-Negative Bacteria from Aerobic Blood Culture Bottles Containing Antibiotic Binding Resins after Exposure to β-Lactam and Fluoroquinolone Concentrations
Abstract
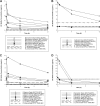
Blood culture bottles containing antibiotic binding resins are routinely used to minimize artificial sterilization in the presence of antibiotics. However, the resin binding kinetics can differ between antibiotics and concentrations. This study assessed the impact of clinically meaningful peak, midpoint, and trough concentrations of meropenem, imipenem, cefepime, cefazolin, levofloxacin, and piperacillin-tazobactam on the recovery of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae from resin-containing BacT/Alert FA Plus and Bactec Aerobic/F blood culture bottles. P. aeruginosa-inoculated bottles alarmed positive in 4/20 (20%), 16/20 (80%), and 20/20 (100%) of those with peak, midpoint, and trough concentrations of antipseudomonal agents, respectively (P ≤ 0.001). E. coli was recovered from 8/24 (33%), 11/24 (46%), and 14/24 (58%) of bottles with peak, midpoint, and trough concentrations, respectively (P = 0.221). K. pneumoniae was recovered from 8/16 (50%) at all concentrations of the studied antibiotics (P = 1.0). BacT/Alert and Bactec bottles inoculated with antibiotics and P. aeruginosa had similar times to detection (TTD) (P = 0.352); however, antibiotic-containing BacT/Alert bottles had a shorter TTD compared with antibiotic-containing Bactec bottles for E. coli (P = 0.026) and K. pneumoniae (P ≤ 0.001). Pathogen recovery in BacT/Alert FA Plus and Bactec Aerobic/F blood culture bottles containing antibiotic binding resins was greatly reduced in the presence of antibiotics, especially at higher concentrations. These data support the practice of drawing blood cultures immediately before an antibiotic dose to maximize the chances of pathogen recovery.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae; antimicrobial stewardship; bacteremia; carbapenem; cephalosporin; levofloxacin; piperacillin.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally ME, Rochwerg B, Rubenfeld GD, Angus DC, Annane D, Beale RJ, Bellinghan GJ, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith C, De Backer DP, French CJ, Fujishima S, Gerlach H, Hidalgo JL, Hollenberg SM, Jones AE, Karnad DR, Kleinpell RM, Koh Y, Lisboa TC, Machado FR, Marini JJ, Marshall JC, Mazuski JE, McIntyre LA, McLean AS, Mehta S, Moreno RP, Myburgh J, Navalesi P, Nishida O, Osborn TM, Perner A, Plunkett CM, Ranieri M, Schorr CA, Seckel MA, Seymour CW, Shieh L, Shukri KA, Simpson SQ, Singer M, Thompson BT, Townsend SR, Van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Wiersinga WJ, Zimmerman JL, Dellinger RP. 2017. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med 45:486–552. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002255. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zadroga R, Williams DN, Gottschall R, Hanson K, Nordberg V, Deike M, Kuskowski M, Carlson L, Nicolau DP, Sutherland C, Hansen GT. 2013. Comparison of 2 blood culture media shows significant differences in bacterial recovery for patients on antimicrobial therapy. Clin Infect Dis 56:790–797. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis1021. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials