Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis following varicella-zoster virus infection: Case report of effective treated both in clinical symptom and neuroimaging
- PMID: 31342665
- PMCID: PMC6749488
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1374
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis following varicella-zoster virus infection: Case report of effective treated both in clinical symptom and neuroimaging
Abstract
Introduction: Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) is an idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system (CNS). Early treatment is the key for neurological recovery.
Methods: A case of ADEM associated with varicella-zoster virus infection was presented, in which magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examinations were included.
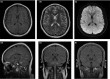
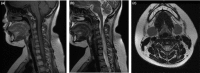
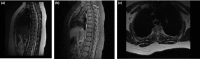
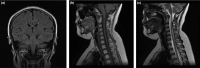
Results: Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain revealed multiple hyperintense lesions at the subcortical level on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR), and MRI of the spinal cord revealed longitudinally segmented hyperintense lesions at the spinal cord on T2-weighted images. The patient was treated with methylprednisolone and gancyclovir, and had a favorable recovery. Subsequent MRI of the brain and cervical cord showed the previous abnormal hyperintensities had markedly disappeared.
Conclusion: A rare case of ADEM with longitudinal segmented hyperintense lesions at the spinal cord on T2-weighted images was presented. Excellent response to ADEM treatment with high-dose steroids was reported resulting in a remarkable neurological recovery. A long-term follow-up is needed for prognosis.
Keywords: acute disseminated encephalomyelitis; central nervous system; multiple sclerosis; neuroimaging.
© 2019 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

