Cardiopulmonary fitness predicts postoperative major morbidity after esophagectomy for patients with cancer
- PMID: 31342676
- PMCID: PMC6656866
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.14174
Cardiopulmonary fitness predicts postoperative major morbidity after esophagectomy for patients with cancer
Abstract
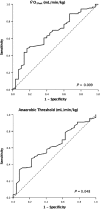
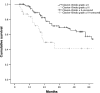
Surgery for radical treatment of esophageal cancer (EC) carries significant inherent risk. The objective identification of patients who are at high risk of complications is of importance. In this study the prognostic value of cardiopulmonary fitness variables (CPF) derived from cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) was assessed in patients undergoing potentially curative surgery for EC within an enhanced recovery program. OC patients underwent preoperative CPET using automated breath-by-breath respiratory gas analysis, with measurements taken during a ramped exercise test on a bicycle. The prognostic value of , Anaerobic Threshold (AT) and VE/VCO2 derived from CPET were studied in relation to post-operative morbidity, which was collected prospectively, and overall survival. Consecutive 120 patients were included for analysis (median age 65 years, 100 male, 75 neoadjuvant therapy). Median AT in the cohort developing major morbidity (Clavien-Dindo classification >2) was 10.4 mL/kg/min compared with 11.3 mL/kg/min with no major morbidity (P = 0.048). Median in the cohort developing major morbidity was 17.0 mL/kg/min compared with 18.7 mL/kg/min in the cohort (P = 0.009). optimum cut-off was 17.0 mL/kg/min (sensitivity 70%, specificity 53%) and for AT was 10.5 mL/kg/min (sensitivity 60%, specificity 44%). Multivariable analysis revealed to be the only independent factor to predict major morbidity (OR 0.85, 95% CI 0.75-0.97, P = 0.018). Cumulative survival was associated with operative morbidity severity (χ2 = 4.892, df = 1, P = 0.027). These results indicate that as derived from CPET is a significant predictor of major morbidity after oesophagectomy highlighting the physiological importance of cardiopulmonary fitness.
Keywords: Cardiopulmonary fitness; esophageal cancer; morbidity; prognosis.
© 2019 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- American Thoracic Society , American College of Chest Physicians . 2003. ATS/ACCP statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 167:211–277. - PubMed
-
- Ausania, F. , Snowden C. P., Prentis J. M., Holmes L. R, Jaques B. C, White S. A, et al. 2012. Effects of low cardiopulmonary reserve on pancreatic leak following pancreaticoduodenectomy. Br. J. Surg. 99:1290–1294. - PubMed
-
- Davison, G. W. , Ashton T., McEneny J., Young I. S., Davies B., and Bailey D. M.. 2012. Critical difference applied to exercise‐induced oxidative stress: the dilemma of distinguishing biological from statistical change. J. Physiol. Biochem. 68:377–384. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous