Modeling nitrogen and phosphorus export with InVEST model in Bosten Lake basin of Northwest China
- PMID: 31344114
- PMCID: PMC6657891
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220299
Modeling nitrogen and phosphorus export with InVEST model in Bosten Lake basin of Northwest China
Abstract
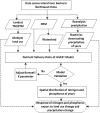
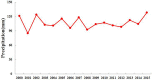
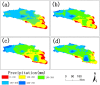
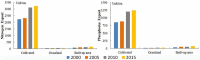
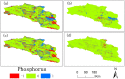
Bosten Lake is an important region of Northwest China that has transformed from a freshwater lake to a saltwater lake since the 1970s. The water quality in the Bosten Lake basin is important for social and economic development, and nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) are the key indicators of water quality. The land use data, precipitation data and Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data with the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs (InVEST) model were used to simulate the N and P exports of the Bosten Lake basin. The spatial and temporal dynamics of nitrogen and phosphorus exports, and the response of nitrogen and phosphorus exports to land use change and precipitation change were analyzed between 2000 and 2015. The results show that the amount of N and P exports increased during 2000-2015, and the N and P exports are mainly distributed around Bosten Lake. The N and P exports are greatly affected by cultivated land, built-up areas and grassland, while they are less affected by other land use types. The high precipitation areas with small exports of N and P are mainly distributed in mountain areas, while small precipitation areas with large exports of N and P are distributed in plains where the cultivated land and built-up areas are concentrated. The InVEST model can be used in Northwest China, and the statistical downscaling of reanalysis precipitation data can be used in the InVEST model to improve the simulation accuracy in the data scarce regions of Northwest China.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


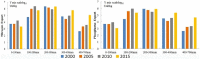


Similar articles
-
Source apportionment of nitrogen and phosphorus from non-point source pollution in Nansi Lake Basin, China.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Jul;25(19):19101-19113. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1956-8. Epub 2018 May 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29725920
-
Improvements in the InVEST water purification model for detecting spatio-temporal changesintotal nitrogen and total phosphorus discharges in the Huai river watershed, China.J Environ Manage. 2024 Aug;366:121918. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121918. Epub 2024 Jul 20. J Environ Manage. 2024. PMID: 39033624
-
Improved export coefficient model for identification of watershed environmental risk areas.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Mar;30(12):34649-34668. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24499-z. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36515872
-
Distribution characteristics of non-point source pollution of TP and identification of key source areas in Nanyi Lake (China) Basin: based on InVEST model and source list method.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Nov;30(55):117464-117484. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-30405-y. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37872342
-
Source appointment at large-scale and ungauged catchment using physically-based model and dynamic export coefficient.J Environ Manage. 2023 Jan 15;326(Pt B):116842. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116842. Epub 2022 Nov 24. J Environ Manage. 2023. PMID: 36436245 Review.
Cited by
-
Impacts of land use change on carbon storage in the Guangxi Beibu Gulf Economic Zone based on the PLUS-InVEST model.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 22;15(1):6468. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89407-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39987139 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Future Water Yield and Water Purification Services in Data Scarce Region of Northwest China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 25;18(17):8960. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18178960. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34501550 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the impact of land use change on habitat quality in Zhongwei through multiscenario simulation using the PLUS and InVEST models.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 10;15(1):12355. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90965-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40210883 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang C, Xu J, Chen Y, Li W. An approach to simulate the climate-driven streamflow in the data-scarce mountain basins of Northwest China. J Earth Syst Sci. 2019; 128(4): 95 10.1007/s12040-019-1117-6 - DOI
-
- Xu J, Wang C, Li W, Zuo J. Multi-temporal scale modeling on climatic-hydrological processes in data-scarce mountain basins of Northwest China. Arab J Geosci. 2018; 11: 423 10.1007/s12517-018-3784-z - DOI
-
- Chen Y, Yang Q, Luo Y, Shen Y, Pan X, Li L, et al. Ponder on the issues of water resources in the arid region of northwest China. Arid Land Geogr. 2012; 35(1): 1–9. (In Chinese)
-
- Duan W, He B, Nover D, Yang G, Chen W, Meng H, et al. Water Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Identification of the Eastern Poyang Lake Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. Sustainability. 2016; 8(2): 133 10.3390/su8020133 - DOI
-
- Chen Y, Li Z, Fan Y, Wang H, Fang G. Research progress on the impact of climate change on water resources in the arid region of Northwest China. Acta Geogr Sin. 2014; 69(9):1295–1304. (In Chinese)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

