Long-Term Visual Outcomes for Small Uveal Melanoma Staged T1 Treated by Proton Beam Radiotherapy
- PMID: 31344948
- PMCID: PMC6721317
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11081047
Long-Term Visual Outcomes for Small Uveal Melanoma Staged T1 Treated by Proton Beam Radiotherapy
Abstract
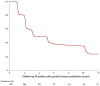
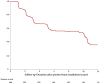
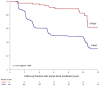
There is increasing evidence of the survival benefit of treating uveal melanoma in an early stage, however it is important to discuss with the patient the associated risk of visual loss. We investigated visual outcomes for uveal melanomas staged T1 (T1UM) treated by proton beam radiotherapy (PBR) as a function of their distance to fovea-optic disc. This retrospective study included a cohort of 424 patients with T1UM treated with PBR between 1991 and 2010 with at least a 5-year follow-up. Visual acuity (VA) was analyzed for patients with posterior edge of tumor located at ≥3 mm (GSup3) or <3 mm (GInf3) from fovea-optic disc. The mean follow-up duration was 122 months, no tumor recurrence was observed. The mean baseline and final VA were 20/25 and 20/32 for GSup3 (n = 75), and 20/40 and 20/80 for GInf3 (n = 317) respectively. The frequency of a 20/200 or greater visual conservation was 93.2%(CI95%:87.7-99.1) and 60.1%(CI95%:54.9-65.9) for GSup3 and GInf3 respectively. This difference between groups was statistically significant (p < 0.001). The risk factors for significant VA loss (less than 20/200) were GInf3 location (p < 0.001), tumor touching optic disc (p = 0.04), initial VA inferior to 20/40 (p < 0.001), documented growth (p = 0.002), and age greater than 60 years (p < 0.001). In summary, PBR for T1UM yields excellent tumor control and good long-term visual outcomes for tumors located ≥3 mm from fovea-optic disc.
Keywords: proton beam radiotherapy 3; staged T1 2; uveal melanoma 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Damato B. Ocular treatment of choroidal melanoma in relation to the prevention of metastatic death A personal view. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018;66:187–199. - PubMed
-
- Desjardins L., Lumbroso-Le R.L., Levy-Gabriel C., Cassoux N., Dendale R., Mazal A., Delacroix S., Sastre X., Plancher C., Asselain B. Treatment of uveal melanoma by accelerated proton beam. Dev. Ophthalmol. 2012;49:41–57. - PubMed
-
- Dendale R., Lumbroso-Le R.L., Noel G., Feuvret L., Levy C., Delacroix S., Meyer A., Nauraye C., Mazal A., Mammar H., et al. Proton beam radiotherapy for uveal melanoma: results of Curie Institut-Orsay proton therapy center (ICPO) Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006;65:780–787. - PubMed
-
- Shields C.L., Sioufi K., Srinivasan A., Nicola M., Masoomian B., Barna L.E., Bekerman V.P., Say E.A.T., Mashayekhi A., Emrich J., et al. Visual Outcome and Millimeter Incremental Risk of Metastasis in 1780 Patients with Small Choroidal Melanoma Managed by Plaque Radiotherapy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018;136:1325–1333. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lane A.M., Kim I.K., Gragoudas E.S. Proton irradiation for peripapillary and parapapillary melanomas. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011;129:1127–1130. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

