Using joint models to disentangle intervention effect types and baseline confounding: an application within an intervention study in prodromal Alzheimer's disease with Fortasyn Connect
- PMID: 31345172
- PMCID: PMC6659198
- DOI: 10.1186/s12874-019-0791-z
Using joint models to disentangle intervention effect types and baseline confounding: an application within an intervention study in prodromal Alzheimer's disease with Fortasyn Connect
Abstract
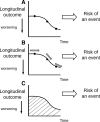
Background: Many prodromal Alzheimer's disease trials collect two types of data: the time until clinical diagnosis of dementia and longitudinal patient information. These data are often analysed separately, although they are strongly associated. By combining the longitudinal and survival data into a single statistical model, joint models can account for the dependencies between the two types of data.
Methods: We illustrate the major steps in a joint modelling approach, motivated by data from a prodromal Alzheimer's disease study: the LipiDiDiet trial.
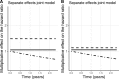
Results: By using joint models we are able to disentangle baseline confounding from the intervention effect and moreover, to investigate the association between longitudinal patient information and the time until clinical dementia diagnosis.
Conclusions: Joint models provide a valuable tool in the statistical analysis of clinical studies with longitudinal and survival data, such as in prodromal Alzheimer's disease trials, and have several added values compared to separate analyses.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Baseline imbalance; Fortasyn; Intervention effect; Joint model.
Conflict of interest statement
FO, SS and AH are employees of Danone Nutricia Research. HS and TH were supported by a grant from the European Commission for the LipiDiDiet study (FP7-211696 LipiDiDiet). HS has served as advisory board member for ACImmune and MERCK. Institution, UEF, has received funding from Nutricia for extension studies of LipiDiDiet Trial (no personal payment). Author DR declares to have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Munro CE, Donovan NJ, Amariglio RE, Papp KV, Marshall GA, Rentz DM, Pascual-Leone A, Sperling RA, Locascio JJ, Vannini P. The impact of awareness of and concern about memory performance on the prediction of progression from mild cognitive impairment to alzheimer disease dementia. Am J Geriatr Psychiatr. 2018;26(8):896–904. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2018.04.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baldeiras I, Santana I, Leitão MJ, Gens H, Pascoal R, Tábuas-Pereira M, Beato-Coelho J, Duro D, Almeida MR, Oliveira CR. Addition of the A β42/40 ratio to the cerebrospinal fluid biomarker profile increases the predictive value for underlying alzheimer’s disease dementia in mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. 2018;10(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0362-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

