Intermittent Hypoxemia in Preterm Infants
- PMID: 31345546
- PMCID: PMC6662623
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clp.2019.05.006
Intermittent Hypoxemia in Preterm Infants
Abstract
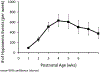
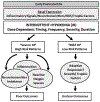
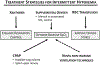
Intermittent hypoxemia (IH) events are common during early postnatal life, particularly in preterm infants. These events have been associated with multiple morbidities, including retinopathy of prematurity, sleep disordered breathing, neurodevelopmental impairment, and mortality. The relationship between IH and poor outcomes may depend on the patterns (frequency, duration, and timing) of the IH events. Current treatment modalities used in the clinical setting have been only partially successful in reducing the incidence of apnea and accompanying IH, but the risks and benefits of more aggressive interventions should include knowledge of the relationship between IH and morbidity.
Keywords: Hypoxia; Intermittent hypoxemia; Neurodevelopmental impairment; Outcomes; Pulse oximetry; Retinopathy of prematurity.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Gleason CA, Martin RJ, Anderson JV, Carlo WA, Sanniti KJ, Fanaroff AA. Optimal position for a spinal tap in preterm infants. Pediatrics. January 1983;71(1):31–35. - PubMed
-
- Rome ES, Stork EK, Carlo WA, Martin RJ. Limitations of transcutaneous PO2 and PCO2 monitoring in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. August 1984;74(2):217–220. - PubMed
-
- Solimano AJ, Smyth JA, Mann TK, Albersheim SG, Lockitch G. Pulse oximetry advantages in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. November 1986;78(5):844–849. - PubMed
-
- Ramanathan R, Durand M, Larrazabal C. Pulse oximetry in very low birth weight infants with acute and chronic lung disease. Pediatrics. April 1987;79(4):612–617. - PubMed
-
- Brockmann PE, Wiechers C, Pantalitschka T, Diebold J, Vagedes J, Poets CF. Under-recognition of alarms in a neonatal intensive care unit. Archives of disease in childhood. Fetal and neonatal edition. November 2013;98(6):F524–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

