IFN-γ selectively suppresses a subset of TLR4-activated genes and enhancers to potentiate macrophage activation
- PMID: 31346169
- PMCID: PMC6658531
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11147-3
IFN-γ selectively suppresses a subset of TLR4-activated genes and enhancers to potentiate macrophage activation
Abstract
Activation of macrophage proinflammatory and antimicrobial phenotypes is regulated by IFN-γ and LPS via synergistic induction of canonical, inflammatory NF-κB target genes. However, whether IFN-γ negatively regulates components of the LPS response, and how this may affect macrophage activation, is still unclear. Here we use combined transcriptomic and epigenomic approaches to find that IFN-γ selectively abrogates LPS-induced feedback and alters macrophage metabolic pathways by suppressing TLR4-mediated gene activation. In contrast to superinduction of inflammatory genes via enhancers that bind IRF1 and STAT1, IFN-γ represses target enhancers that bind STAT3. TLR4-activated but IFN-γ-suppressed enhancers comprise two subsets discernable by differential regulation of histone acetylation and recruitment of STAT3, CDK8 and cohesin. Our findings thus show that IFN-γ suppresses feedback inhibitory and metabolic components of TLR responses to enhance macrophage activation; they also provide insights for IFN-γ-mediated selective inhibition of TLR4-induced transcription. Such inhibition can contribute to severe and sustained inflammatory responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
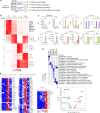
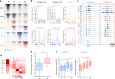


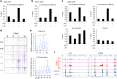

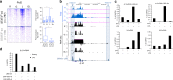
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

