Role of 0.5 M mannitol as an adjuvant with lidocaine with or without epinephrine for inferior alveolar nerve block: A randomized control trial
- PMID: 31346368
- PMCID: PMC6645255
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.55583
Role of 0.5 M mannitol as an adjuvant with lidocaine with or without epinephrine for inferior alveolar nerve block: A randomized control trial
Abstract
Background: The most commonly used local anesthetic in dentistry is lidocaine. For decades, mannitol is the most widely used agent in the management of raised intracranial pressure and as prophylaxis against acute renal failure surgeries.
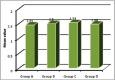
Material and methods: 120 patients were randomly divided into four groups, 30 patients in each group. Group A was administered 2% lidocaine with 1:80000 epinephrine; group B, 2% lidocaine with 1:80000 epinephrine and 0.5 M mannitol; group C, 2% lidocaine and 0.5 M mannitol; and group D (control group), 2% lidocaine for achieving local anesthesia. Extraction of lower erupted tooth was done under inferior alveolar nerve block. Parameters taken were onset of anesthesia, duration of anesthesia and pain. Heft-Parker visual analogue scale was taken to evaluate the pain response during procedure after every 10 minutes until complete return of sensation by probing. The Chi-square test was used to compare the pain among the groups. The continuous variables were compared among the groups by one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey's post-hoc comparison tests. The p-value <0.05 was considered significant.
Results: The onset of tingling sensation was higher among the patients of group C (1.53±0.57) than group B (1.50±0.58), group D (1.48±0.51) and group A (1.45±0.62) but difference among the groups was statistically insignificant (p >0.05). The total time in return of sensation was higher among the patients of group C (70.30±4.34) than group A (65.94±3.45), group B (62.23±7.47) and group D (47.70±8.04) but difference among the groups was found to be statistically significant (p=0.0001). There was no significant (p >0.05) difference in the pain at baseline and at start. No pain was found among all the patients from 10 minutes to subsequent time intervals.
Conclusions: Mannitol was effective in increasing the efficacy of lidocaine as an adjuvant to local anesthetic solution in inferior alveolar nerve block. Key words:Inferior alveolar nerve block, lidocaine, local anesthesia, mannitol.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement:The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- Matsuka Y, Spigleman I. Hyperosmolar solutions selectively block action potentials in rat myelinated sensory fibers: implications for diabetic neuropathy. J Neurophysiology. 2004;91:48–56. - PubMed
-
- Thimmaiah PB, Hegde MN, Bhat GT, Shetty A, Shetty S. Anesthetic efficacy of combination of two percent lidocaine with 1:80000 epinephrine and 0.5 mol/L mannitol for inferior alveolar nerve blocks in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis: In Vivo study. Int Res J Pharm. 2013;4:161–3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources