Circulating microRNAs and endothelial cell migration rate are associated with metabolic syndrome and fitness level in postmenopausal African American women
- PMID: 31347282
- PMCID: PMC6658676
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.14173
Circulating microRNAs and endothelial cell migration rate are associated with metabolic syndrome and fitness level in postmenopausal African American women
Abstract
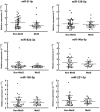
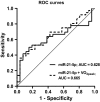
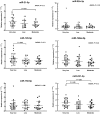
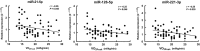
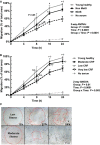
Postmenopausal African American women are at elevated risk for metabolic syndrome (MetS), which predisposes them to cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. Circulating microRNAs (ci-miR) are potential mediators of cardiometabolic diseases also impacted by cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) level. Using real-time quantitative PCR, we compared the expression of vascular-related ci-miRs (miR-21-5p, miR-92a-3p, miR-126-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-150-5p, miR-221-3p) in sedentary, overweight/obese, postmenopausal African American women based on 1) presence (n = 31) or absence (n = 42) of MetS and 2) CRF level (VO2peak ) (Very Low < 18.0 mL·kg-1 ·min-1 [n = 31], Low = 18.0-22.0 mL·kg-1 ·min-1 [n = 24], or Moderate >22.0 mL·kg-1 ·min-1 [n = 18]). Endothelial migration rate in response to subjects' serum was assessed to determine the effect of circulating blood-borne factors on endothelial repair. Ci-miR-21-5p was the only ci-miR that differed between women with MetS compared to those without MetS (0.93 ± 0.43 vs. 1.28 ± 0.71, P = 0.03). There were borderline significant differences (P = 0.06-0.09) in ci-miR-21-5p, 126-5p, and 221-3p levels between the CRF groups, and these three ci-miRs correlated with VO2peak (r = -0.25 to -0.28, P < 0.05). Endothelial migration rate was impaired in response to serum from women with MetS compared to those without after 16-24 h. Serum from women with Moderate CRF induced greater endothelial migration than the Very Low and Low CRF groups after 4 and 16-24 h, that was also not different from a young, healthy reference group. Ci-miR-21-5p is lower in postmenopausal African American women with MetS, while ci-miRs-21-5p, 126-5p, and 221-3p are associated with CRF. Factors which impair endothelial cell migration rate are present in serum of women with MetS, though having Moderate CRF may be protective.
Keywords: Cardiorespiratory fitness; circulating microRNA; endothelium; menopause; metabolic syndrome.
© 2019 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Ahirwar, A. K. , Jain A., Singh A., Goswami B., Bhatnagar M. K., and Bhatacharjee J.. 2015. The study of markers of endothelial dysfunction in metabolic syndrome. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Invest. 24:131–136. - PubMed
-
- Bär, C. , Thum T., and de Gonzalo‐Calvo D.. 2019. Circulating miRNAs as mediators in cell‐to‐cell communication. Epigenomics 11:111–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

